Metaxalone
Metaxalone, sold under the brand name Skelaxin, is a muscle relaxant medication used to relax muscles and relieve pain caused by strains, sprains, and other musculoskeletal conditions.[1] Its exact mechanism of action is not known, but it may be due to general central nervous system depression.[1] It is a moderately strong muscle relaxant, with relatively low incidence of side effects.
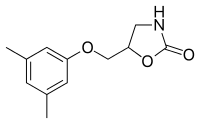 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Skelaxin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682010 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 9.2 (± 4.8) hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.253 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H15NO3 |
| Molar mass | 221.256 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Common side effects include nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, and central nervous system (CNS) side effects, such as dizziness, headache, and irritability.[1]
The metabolism of metaxalone involves enzymes CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 in the cytochrome P450 system. Because many medications are metabolized by enzymes in this system, precaution must be taken when administering it with other medications involving the P450 system to avoid interactions.[2]
Because of the potential for side effects, this drug is considered a high risk in the elderly.
Pharmacokinetics
Metaxalone exhibits increased bioavailability when taken with food.[3] Specifically, in one study, compared to fasted conditions, the presence of food at the time of drug administration increased Cmax by 77.5%, AUC0-t by 23.5%, and AUC0-∞ by 15.4%.[4] Metaxalone is a substrate of CYP1A2 and CYP2C19, an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A, and an inducer of CYP1A2 and CYP3A4.[2]
Assay
A literature survey reveals very few methods are reported for the determination of metaxalone to date. Nirogi et al.[4] reported a liquid chromatographic method coupled to tandem mass spectrometry for the quantification of metaxalone in human plasma. A stability-indicating HPLC method was introduced by P.K. Sahu et al.[5] Metaxalone has been used as an internal standard for few analytical methods.[6][7]
References
- "Skelaxin- metaxalone tablet". DailyMed. 27 April 2018. Retrieved 23 October 2020.
- United States Patent No. 7,378,434, by Jie Du, et al
- Skelaxin Package Insert
- Nirogi RV, Kandikere VN, Shukla M, Mudigonda K, Shrivastava W, Datla PV (May 2006). "Quantification of Metaxalone in Human Plasma by Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry". J Anal Toxicol. 30 (4): 245–51. doi:10.1093/jat/30.4.245. PMID 16803662.
- Sahu, Prafulla Kumar; Annapurna, M. Mathrusri; Kumar, Sahoo Dillip (2011). "Development and Validation of Stability Indicating RP-HPLC Method for the Determination of Metaxalone in Bulk and its Pharmaceutical Formulations". e-Journal of Chemistry. 8 (s1): S439–S447. doi:10.1155/2011/645710.
- Mistri, HN; Jangid, AG; Pudage, A; Gomes, N; Sanyal, M; Shrivastav, P (15 June 2007). "High throughput LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of lamivudine, stavudine and nevirapine in human plasma". Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences. 853 (1–2): 320–32. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.03.047. PMID 17481969.
- Mistri, HN; Jangid, AG; Pudage, A; Shrivastav, P (15 March 2008). "HPLC-ESI-MS/MS validated method for simultaneous quantification of zopiclone and its metabolites, N-desmethyl zopiclone and zopiclone-N-oxide in human plasma". Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences. 864 (1–2): 137–48. doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2008.02.004. PMID 18313371.
External links
- "Metaxalone". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.