Zoxazolamine
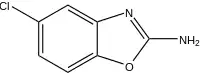
Zoxazolamine (INN, USAN, BAN) (brand name Contrazole, Deflexol, Flexin, Miazol, Uri-Boi, Zoxamine, Zoxine) is a muscle relaxant that is no longer marketed.[1][2] It was synthesized in 1953 and introduced clinically in 1955 but was withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity.[1][2][3] One of its active metabolites, chlorzoxazone, was found to show less toxicity, and was subsequently marketed in place of zoxazolamine.[3] These drugs activate IKCa channels.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | McN-485 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H5ClN2O |
| Molar mass | 168.58 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 48–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Kar A (1 January 2005). Medicinal Chemistry. New Age International. pp. 185–. ISBN 978-81-224-1565-0.
- Lowry W (6 December 2012). Forensic Toxicology: Controlled Substances and Dangerous Drugs. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 166–. ISBN 978-1-4684-3444-6.
- Offermanns S (14 August 2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 996–. ISBN 978-3-540-38916-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.