Febarbamate
Febarbamate (INN; Solium, Tymium), also known as phenobamate, is an anxiolytic and tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe by itself and as part of a combination drug formulation called tetrabamate.[1][2][3][4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | MS-543 |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.032.919 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
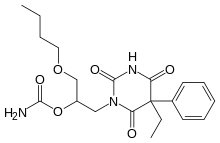
| Formula | C20H27N3O6 |
| Molar mass | 405.451 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
See also
References
- World Health Organization (2004). "The use of stems in the selection of International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substance" (PDF).
- Index nominum 2000: international drug directory. Taylor & Francis US. 2000. p. 427. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. Retrieved 26 November 2011.
- Gentili E (March 1972). "[Therapeutic effects of a new psycholeptic agent (febarbamate, Solium) in pediatrics]". Minerva Medica (in Italian). 63 (18): 1058–60. PMID 5016064.
- Morton I, Hall JM (1999). Concise dictionary of pharmacological agents: properties and synonyms. Springer. p. 118. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9. Retrieved 26 November 2011.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.