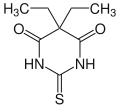
Thiobarbital
Thiobarbital is a drug which is a barbiturate derivative. It is the thiobarbiturate analogue of barbital.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.929 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H12N2O2S |
| Molar mass | 200.259 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
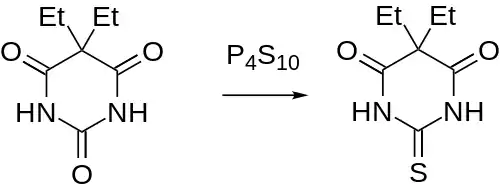
Synthesis
It is of note that although the drug can be prepared by the above route (cf e.g. thialbarbital), reaction of barbital with phosphorus pentasulfide constitutes an alternative route to thiobarbital.
References
- Fischer E, Dilthey A (1904). "Ueber C-Dialkylbarbitursäuren und über die Ureïde der Dialkylessigsäuren". Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie. 335 (3): 334–368. doi:10.1002/jlac.19043350303.
- Carrington HC (1944). "45. The action of phosphorus pentasulphide on barbituric acids". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 124. doi:10.1039/JR9440000124.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.