Sulazepam
Sulazepam is a benzodiazepine derivative. It is the thioamide derivative of diazepam. It is metabolised into diazepam, desmethyldiazepam and oxydiazepam. It has sedative, muscle relaxant, hypnotic, anticonvulsant and anxiolytic properties like those of other benzodiazepines.[1][2] It was never marketed.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H13ClN2S |
| Molar mass | 300.80 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Synthesis
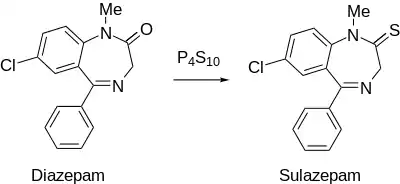
Sulazepam synthesis:[3] U.S. Patent 3,141,890
Treatment of diazepam with phosphorus pentasulfide produces the corresponding thionamide, sulazepam.
See also
References
- "sulazepam". psychotropics.dk. 2003. Retrieved 29 December 2008.
- Golovenko NI, Zin'kovskii VG (September 1976). "[Analysis of the structure of the components of the convulsive action of corazole following administration of sulazepam and its metabolites to mice]" [Analysis of the structure of the components of the convulsive action of corazole following administration of sulazepam and its metabolites to mice]. Biulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii I Meditsiny (in Russian). 82 (9): 1078–81. PMID 11012.
- Archer GA, Sternbach LH (1964). "Quinazolines and 1,4-Benzodiazepines. XVI. Synthesis and Transformations of 5-Phenyl-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thiones". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 29: 231. doi:10.1021/jo01024a511.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.