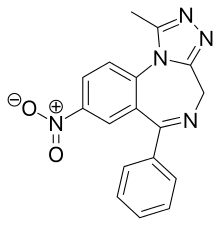
Nitrazolam
Nitrazolam is a triazolobenzodiazepine (TBZD) , which are benzodiazepine (BZD) derivatives,[1] that has been sold online as a designer drug.[2][3]
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H13N5O2 |
| Molar mass | 319.324 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
It is closely related to Clonazolam or Flunitrazolam, only differing by the removal of a Chlorine or Fluorine group respectively at the benzene ring.
A study in mice indicated that nitrazolam can be several times more potent than diazepam as an antagonist of electroshock-induced tonic-extensor convulsions but less potent than diazepam at preventing the righting reflex.[4]
Nitrazolam has been used as an example compound to demonstrate the microscale synthesis of reference materials utilizing polymer‐supported reagents.[5]
Legal Status
United Kingdom
In the UK, nitrazolam has been classified as a Class C drug by the May 2017 amendment to The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 along with several other designer benzodiazepine drugs.[6]
See also
- Adinazolam
- Alprazolam (licensed)
- Flubromazolam
- Nifoxipam
- Nitemazepam
- Pyrazolam
- Triazolam (licensed)
References
- Hester Jr JB (19 October 1976). "Patent US3987052 - 6-Phenyl-4H-s-triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepines". The Upjohn Company.
- "Nitrazolam". New Synthetic Drugs Database.
- Moosmann B, Bisel P, Franz F, Huppertz LM, Auwärter V (November 2016). "Characterization and in vitro phase I microsomal metabolism of designer benzodiazepines - an update comprising adinazolam, cloniprazepam, fonazepam, 3-hydroxyphenazepam, metizolam and nitrazolam". Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 51 (11): 1080–1089. Bibcode:2016JMSp...51.1080M. doi:10.1002/jms.3840. PMID 27535017.
- Hester JB, Rudzik AD, Kamdar BV (November 1971). "6-phenyl-4H-s-triazolo[4,3-a][1,4]benzodiazepines which have central nervous system depressant activity". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 14 (11): 1078–81. doi:10.1021/jm00293a015. PMID 5165540.
- Dowling G, Kavanagh PV, Eckhardt HG, Twamley B, Hessman G, McLaughlin G, et al. (March 2018). "An approach to shortening the timeframe between the emergence of new compounds on the drugs market and the availability of reference standards: The microscale syntheses of nitrazolam and clonazolam for use as reference materials, utilizing polymer-supported reagents" (PDF). Drug Testing and Analysis. 10 (7): 1198–1208. doi:10.1002/dta.2383. PMID 29542872.
- "The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Amendment) Order 2017".