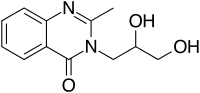
Diproqualone
Diproqualone is a quinazolinone class GABAergic and is an analogue of methaqualone developed in the late 1950s by a team at Nogentaise de Produits Chimique. It was marketed primarily in France and some other European countries. It has sedative, anxiolytic, antihistamine and analgesic properties, resulting from its agonist activity at the β subtype of the GABAa receptor, antagonist activity at all histamine receptors, inhibition of the cyclooxygenase-1 enzyme, and possibly its agonist activity at both the sigma-1 receptor and sigma-2 receptor (the function of these receptors and their clinical relevance has not yet been determined). Diproqualone is used primarily for the treatment of inflammatory pain associated with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, and more rarely for treating insomnia, anxiety and neuralgia.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.048.240 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H14N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 234.251 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Diproqualone is the only analogue of methaqualone that is still in widespread clinical use, due to its useful anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects in addition to the sedative and anxiolytic actions common to other drugs of this class. There are still some concerns about the potential of diproqualone for abuse and overdose, and so it is not sold as a pure drug but only as the camphosulfonate salt in combination mixtures with other medicines such as ethenzamide.
See also
- Methaqualone
- Afloqualone
- Etaqualone
- Methylmethaqualone
- Mecloqualone
- Mebroqualone
- Cloroqualone
- Gamma-Aminobutyric acid