Triclofos
Triclofos is a sedative drug used rarely for treating insomnia.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.624 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
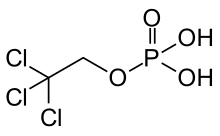
| Formula | C2H4Cl3O4P |
| Molar mass | 229.37 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Triclofos is a prodrug which is metabolised in the liver into the active drug trichloroethanol. The half-life of triclofos is fairly long and it may cause drowsiness the next day. Trichloroethanol may cause liver damage and triclofos should not be used for extended periods.
Triclofos is no longer available in the United States.[2]
Side effects
Side effects may include: headache, rash, dizziness, flatulence, confusion, nightmares, dependence, diarrhoea, constipation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and ataxia.
References
- Erhorn S (2007). "Triclofos". xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference. Elsevier. pp. 1–4. doi:10.1016/B978-008055232-3.62797-7. ISBN 978-0-08-055232-3. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
- "Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs". www.accessdata.fda.gov. Retrieved 29 February 2020.
| Alcohols |
|
|---|---|
| Barbiturates |
|
| Benzodiazepines |
|
| Carbamates | |
| Flavonoids |
|
| Imidazoles | |
| Kava constituents |
|
| Monoureides |
|
| Neuroactive steroids |
|
| Nonbenzodiazepines | |
| Phenols | |
| Piperidinediones | |
| Pyrazolopyridines | |
| Quinazolinones | |
| Volatiles/gases |
|
| Others/unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • GABA receptor modulators • GABA metabolism/transport modulators | |
Glycine receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||
| |||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.