Aceburic acid
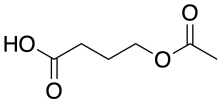
Aceburic acid (INN), also known as 4-acetoxybutanoic acid or 4-hydroxybutyric acid acetate, is drug described as an analgesic which was never marketed.[1] It is the acetyl ester of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB, which is 4-hydroxybutanoic acid),[1] and based on its structural relation to GHB, is likely to behave as a prodrug to it.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6H10O4 |
| Molar mass | 146.142 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
See also
- 1,4-Butanediol (1,4-BD)
- 1,6-Dioxecane-2,7-dione
- γ-Butyrolactone (GBL)
- γ-Hydroxybutyraldehyde (GHBAL)
- γ-Valerolactone (GVL)
- Aceturic acid
- Aceglutamide
- Ethyl acetoxy butanoate
References
- Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ (21 November 1996). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents. CRC Press. pp. 1052–. ISBN 978-0-412-46630-4.
GABA receptor modulators | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionotropic |
| ||||
| Metabotropic |
| ||||
| |||||
GHB receptor modulators | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||
| Transporter (blockers) |
| ||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.