SKF-97,541
SKF-97,541 is a compound used in scientific research which acts primarily as a selective GABAB receptor agonist.[1] It has sedative effects in animal studies and is widely used in research into potential treatment of various types of drug addiction.[2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.229.655 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
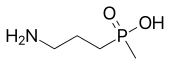
| Formula | C4H12NO2P |
| Molar mass | 137.119 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Seabrook GR, Howson W, Lacey MG (December 1990). "Electrophysiological characterization of potent agonists and antagonists at pre- and postsynaptic GABAB receptors on neurones in rat brain slices". British Journal of Pharmacology. 101 (4): 949–57. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14186.x. PMC 1917862. PMID 1964824.
- Jackson GL, Kuehl D (May 2002). "The GABA(B) antagonist CGP 52432 attenuates the stimulatory effect of the GABA(B) agonist SKF 97541 on luteinizing hormone secretion in the male sheep". Experimental Biology and Medicine. 227 (5): 315–20. doi:10.1177/153537020222700503. PMID 11976401. S2CID 35467974.
- Besheer J, Lepoutre V, Hodge CW (July 2004). "GABA(B) receptor agonists reduce operant ethanol self-administration and enhance ethanol sedation in C57BL/6J mice". Psychopharmacology. 174 (3): 358–66. doi:10.1007/s00213-003-1769-3. PMID 14985930. S2CID 25036152.
- Carter LP, Chen W, Coop A, Koek W, France CP (May 2006). "Discriminative stimulus effects of GHB and GABA(B) agonists are differentially attenuated by CGP35348". European Journal of Pharmacology. 538 (1–3): 85–93. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.03.039. PMID 16647701.
- Koek W, Mercer SL, Coop A (June 2007). "Cataleptic effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB), its precursor gamma-butyrolactone (GBL), and GABAB receptor agonists in mice: differential antagonism by the GABAB receptor antagonist CGP35348". Psychopharmacology. 192 (3): 407–14. doi:10.1007/s00213-007-0718-y. PMID 17277933. S2CID 25049526.
- Koek W, Mercer SL, Coop A, France CP (September 2009). "Behavioral effects of gamma-hydroxybutyrate, its precursor gamma-butyrolactone, and GABA(B) receptor agonists: time course and differential antagonism by the GABA(B) receptor antagonist 3-aminopropyl(diethoxymethyl)phosphinic acid (CGP35348)". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 330 (3): 876–83. doi:10.1124/jpet.109.151845. PMC 2729800. PMID 19564487.
- Frankowska M, Nowak E, Filip M (2009). "Effects of GABAB receptor agonists on cocaine hyperlocomotor and sensitizing effects in rats". Pharmacological Reports. 61 (6): 1042–9. doi:10.1016/s1734-1140(09)70166-5. PMID 20081239.
- Ranson DC, Ayoub SS, Corcoran O, Casalotti SO (2020). "Pharmacological targeting of the GABA B receptor alters Drosophila's behavioural responses to alcohol". Addiction Biology. 25 (2): e12725. doi:10.1111/adb.12725. PMC 7050513. PMID 30761704.
- Gawlińska K, Jastrzębska J, Gamberini S, Gawliński D, Pieniążek R, Suder A, Wydra K, Frankowska M (September 2020). "The impact of GABAB receptors and their pharmacological stimulation on cocaine reinforcement and drug-seeking behaviors in a rat model of depression". European Journal of Pharmacology. 883: 173324. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173324. PMID 32621910.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.