α5IA
α5IA (LS-193,268) is a nootropic drug invented in 2004 by a team working for Merck, Sharp and Dohme, which acts as a subtype-selective inverse agonist at the benzodiazepine binding site on the GABAA receptor. It binds to the α1, α2, α3 and α5 subtypes.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LS-193,268 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
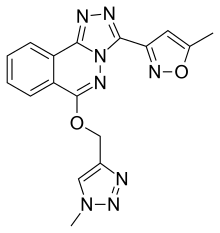
| Formula | C17H14N8O2 |
| Molar mass | 362.353 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
In Vivo Electrophysiology
Recordings of local field potentials indicate that oral administration of α5IA increases the amplitude of sharp wave ripples which are implicated in memory function in adult wild type rats. It is intriguing to note that the increase in ripple amplitude is not seen in adult male TgF344-AD rats which express human β-amyloid precursor protein (with the Swedish mutation) and human presenilin-1 (with a Δ exon 9 mutation). [3]
References
- Sternfeld F, Carling RW, Jelley RA, Ladduwahetty T, Merchant KJ, Moore KW, et al. (April 2004). "Selective, orally active gamma-aminobutyric acidA alpha5 receptor inverse agonists as cognition enhancers". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (9): 2176–9. doi:10.1021/jm031076j. PMID 15084116.
- Street LJ, Sternfeld F, Jelley RA, Reeve AJ, Carling RW, Moore KW, et al. (July 2004). "Synthesis and biological evaluation of 3-heterocyclyl-7,8,9,10-tetrahydro-(7,10-ethano)-1,2,4-triazolo[3,4-a]phthalazines and analogues as subtype-selective inverse agonists for the GABA(A)alpha5 benzodiazepine binding site". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 47 (14): 3642–57. doi:10.1021/jm0407613. PMID 15214791.
- Ratner MH, Downing SS, Guo O, Odamah KE, Stewart TM, Kumaresan V, Robitsek RJ, Xia W, Farb DH (September 2021). "Prodromal dysfunction of α5GABA-A receptor modulated hippocampal ripples occurs prior to neurodegeneration in the TgF344-AD rat model of Alzheimer's disease". Heliyon. 7 (9): e07895. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07895. PMC 8449175. PMID 34568591.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.