Emylcamate
Emylcamate (marketed as Striatran by Merck) is an anxiolytic and muscle relaxant. It was patented in the US in 1961 (US Patent 2,972,564) and advertised for the treatment of anxiety and tension. It was claimed to be superior to meprobamate, which was the market leader at the time. It is no longer prescribed.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
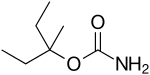
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.002 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 145.202 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
A study of the drug's effects in mice was done in 1959. It concluded that at 50 mg/kg emylcamate gave a 63% decrease in motor activity compared with meprobamate's 32% decrease, a doubling in effective potency. The therapeutic index in mice was also established:
| Meprobamate | Emylcamate | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| 175 | 123 | ED50 (mg/kg) |
| 600 | 550 | LD50 (mg/kg) |
| 3.4 | 4.4 | Therapeutic index |
Emylcamate also has a faster intra-parenteral onset than meprobamate, 3 minutes compared with 35. [1]
References
- Melander B (1959). "Emylcamate, A Potent Tranquillizing Relaxant". Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry. 1 (5): 443–457. doi:10.1021/jm50006a003.
Further reading
- Shorter E (August 2004). "Olhando para trás: um novo caminho possível para a descoberta de drogas em psicofarmacologia" [Looking back: a new possible path for drug discovery in psychopharmacology.] (PDF). Revista de Psiquiatria do Rio Grande do Sul (in Portuguese). 26 (2): 196–203. doi:10.1590/S0101-81082004000200009. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2006-07-21.
External links
- "Emylcamate". The Comparative Toxicogenomics Database.
- "Emylcamate". BIAM (in French).
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.