Irazepine
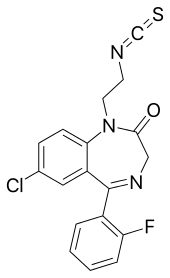
Irazepine (Ro 7-1986/1) is a benzodiazepine derivative containing isothiocyanate functional group.[1] It is a non-competitive benzodiazepine binding site antagonist.[2] Irazepine and other alkylating benzodiazepines, such as kenazepine, bind to brain benzodiazepine receptors in a non-competitive (covalent) fashion in vitro, and may exert a long-lasting anticonvulsant effect.[3]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H13ClFN3OS |
| Molar mass | 373.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Ganellin CR, Triggle DJ, eds. (1999). Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents (1st ed.). London: Chapman & Hall. ISBN 9780412466304.
- Hall IK, Morton JM (1999). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents Properties and Synonyms. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. p. 156. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- Williams EF, Rice KC, Mattson M, Paul SM, Skolnick P (April 1981). "In vivo effects of two novel alkylating benzodiazepines, irazepine and kenazepine". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 14 (4): 487–91. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(81)90307-5. PMID 7232472. S2CID 22221220.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.