Phenylethylidenehydrazine
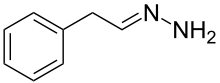
Phenylethylidenehydrazine (PEH), also known as 2-phenylethylhydrazone or β-phenylethylidenehydrazine, is an inhibitor of the enzyme GABA transaminase (GABA-T).[1][2] It is a metabolite of the antidepressant phenelzine and is responsible for its elevation of GABA concentrations.[1] PEH may contribute to phenelzine's anxiolytic effects.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | ~12 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H10N2 |
| Molar mass | 134.182 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
See also
References
- Parent MB, Master S, Kashlub S, Baker GB (January 2002). "Effects of the antidepressant/antipanic drug phenelzine and its putative metabolite phenylethylidenehydrazine on extracellular gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in the striatum". Biochemical Pharmacology. 63 (1): 57–64. doi:10.1016/S0006-2952(01)00856-5. PMID 11754874.
- Duffy S, Nguyen PV, Baker GB (2004). "Phenylethylidenehydrazine, a novel GABA-transaminase inhibitor, reduces epileptiform activity in rat hippocampal slices". Neuroscience. 126 (2): 423–32. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.03.007. PMID 15207360. S2CID 30625470.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.