Raphidovirus
Raphidovirus (likely misspelled Rhaphidovirus) is a genus of viruses, in the family Phycodnaviridae. Alga serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Heterosigma akashiwo virus 01 (HaV01).[1][2]
| Raphidovirus | |
|---|---|
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Varidnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Bamfordvirae |
| Phylum: | Nucleocytoviricota |
| Class: | Megaviricetes |
| Order: | Algavirales |
| Family: | Phycodnaviridae |
| Genus: | Raphidovirus |
Structure
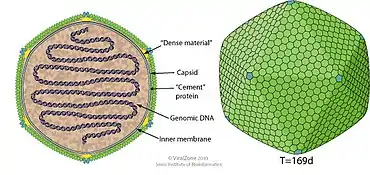
Schematic drawing of a typical Phycodnaviridae virion (cross section and side view)
Viruses in Raphidovirus are enveloped, with icosahedral and round geometries, and T=169 symmetry. The diameter is around 100-220 nm. Genomes are linear, around 295kb in length.[1]
| Genus | Structure | Symmetry | Capsid | Genomic arrangement | Genomic segmentation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raphidovirus | Icosahedral | T=169 | Enveloped | Linear | Monopartite |
Life cycle
Viral replication is nucleo-cytoplasmic. Replication follows the DNA strand displacement model. DNA-templated transcription is the method of transcription. The virus exits the host cell by lysis via lytic phospholipids. Alga serve as the natural host. Transmission routes are passive diffusion.[1]
| Genus | Host details | Tissue tropism | Entry details | Release details | Replication site | Assembly site | Transmission |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raphidovirus | Alga | None | Cell receptor endocytosis | Lysis | Nucleus | Cytoplasm | Passive diffusion |
References
- "Viral Zone". ExPASy. Retrieved 15 June 2015.
- "Virus Taxonomy: 2020 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV). March 2021. Retrieved 22 May 2021.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.