Measles vaccine
.jpg.webp) A child is given a measles vaccine. | |
| Vaccine description | |
|---|---|
| Target disease | Measles virus |
| Type | Attenuated virus |
| Clinical data | |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601176 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
Measles vaccine is a vaccine that prevents measles.[1] Nearly all of those who do not develop immunity after a single dose develop it after a second dose.[1] When rates of vaccination within a population are greater than 92%, outbreaks of measles typically no longer occur; however, they may occur again if rates of vaccination decrease.[1] The vaccine's effectiveness lasts many years.[1] It is unclear if it becomes less effective over time.[1] The vaccine may also protect against measles if given within a couple of days after exposure to measles.[1]
The vaccine is generally safe, even for those with HIV infections.[1][2] Most children do not experience any side effects.[3] Side effects if they do occur are usually mild, such as fever, rash, pain at the site of injection, and joint stiffness; and are short lived.[1][3] Anaphylaxis has been documented in about 3.5–10 cases per million doses.[1] Rates of Guillain–Barré syndrome, autism and inflammatory bowel disease do not appear to be increased by measles vaccination.[1]
The vaccine is available both by itself and in combinations such as the MMR vaccine (a combination with the rubella vaccine and mumps vaccine)[1] or the MMRV vaccine (a combination of MMR with the chickenpox vaccine).[4][5][6] The measles vaccine is equally effective for preventing measles in all formulations, but side effects vary depending with the combination.[1][7] The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends measles vaccine be given at nine months of age in areas of the world where the disease is common, or at twelve months where the disease is not common.[1] Measles vaccine is based on a live but weakened strain of measles.[1] It comes as a dried powder which is mixed with a specific liquid before being injected either just under the skin or into a muscle.[1] Verification that the vaccine was effective can be determined by blood tests.[1]
In 1963, the Edmonston-B strain of measles virus was turned into a vaccine and licensed in the United States.[8] In 1968, an improved and even weaker measles vaccine began to be distributed and has been the only measles vaccine used in the United States since 1968.[8] About 85% of children globally have received this vaccine as of 2013.[9] In 2015, at least 160 countries provided two doses in their routine immunization.[10] The measles vaccine was first introduced in 1963.[11] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[12] The wholesale cost in the developing world is about 0.70 USD per dose as of 2015.[13] As outbreaks easily occur in under-vaccinated populations, the disease is seen as a test of sufficient vaccination within a population.[14]
Medical uses
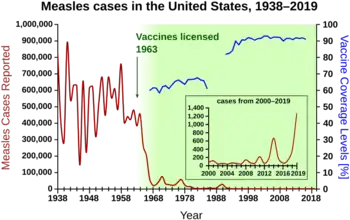
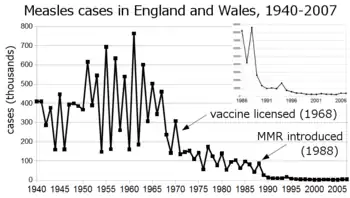
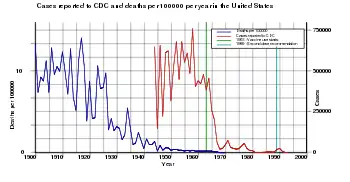
One dose is about 93% effective while two doses of the vaccine are about 97% effective at preventing measles.[2] Before the widespread use of the vaccine, measles was so common that infection was considered "as inevitable as death and taxes."[15] In the United States, reported cases of measles fell from 3 to 4 million with 400 to 500 deaths to tens of thousands per year following introduction of two measles vaccines in 1963 (both an inactivated and a live attenuated vaccine (Edmonston B strain) were licensed for use, see chart at right).[2][16] Increasing uptake of the vaccine following outbreaks in 1971 and 1977 brought this down to thousands of cases per year in the 1980s. An outbreak of almost 30,000 cases in 1990 led to a renewed push for vaccination and the addition of a second vaccine to the recommended schedule. No more than 220 cases were reported in any year from 1997 to 2013, and the disease was believed no longer endemic in the United States.[17][18][19] In 2014, 667 cases were reported.[20]
The benefit of measles vaccination in preventing illness, disability, and death have been well documented. Within the first 20 years of being licensed in the U.S., measles vaccination prevented an estimated 52 million cases of the disease, 17,400 cases of mental retardation, and 5,200 deaths.[21] During 1999–2004, a strategy led by the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF led to improvements in measles vaccination coverage that averted an estimated 1.4 million measles deaths worldwide.[22] The vaccine for measles has led to the near-complete elimination of the disease in the United States and other developed countries.[23] While the vaccine is made with a live virus which can cause side effects, these are far fewer and less serious than the sickness and death caused by measles itself, side effects ranging from rashes to, rarely, convulsions, occur in a small percentage of recipients.[24]
Measles is common worldwide. Although it was declared eliminated from the U.S. in 2000, high rates of vaccination and excellent communication with those who refuse vaccination are needed to prevent outbreaks and sustain the elimination of measles in the U.S.[25] Of the 66 cases of measles reported in the U.S. in 2005, slightly over half were attributable to one unvaccinated teenager who acquired measles during a visit to Romania.[26] This individual returned to a community with many unvaccinated children. The resulting outbreak infected 34 people, mostly children and virtually all unvaccinated; three of them were hospitalized. The public health response required making almost 5,000 phone calls as part of contact tracing, arranging and performing testing as needed, and arranging emergency vaccination for at-risk people who had contact with this person.[25] Taxpayers and local healthcare organizations likely paid more than US$167,000 in direct costs to contain this one outbreak.[25] A major epidemic was averted due to high rates of vaccination in the surrounding communities.[25]
The vaccine has non specific effects such as preventing respiratory infections, that may be greater than those of measles prevention alone. These benefits are greater when the vaccine is given before one year of age. A high titre vaccine resulted in worse outcomes in girls and thus is not recommended by the World Health Organization.[27]
Schedule
Error: Dataset name contains invalid characters.
%252C_OWID.svg.png.webp)
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends two doses of vaccine for all children.[1] In countries with high risk of disease the first dose should be given around nine months of age.[1] Otherwise it can be given at twelve months of age.[1] The second dose should be given at least one month after the first dose.[1] This is often done at age 15 to 18 months.[1] After one dose at the age of nine months 85% are immune, while a dose at twelve months results in 95% immunity.[11]
In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that children aged six to eleven months traveling outside the United States receive their first dose of MMR vaccine before departure[28] and then receive two more doses; one at 12–15 months (12 months for children in high-risk areas) and the second as early as four weeks later.[29] Otherwise the first dose is typically given at 12–15 months and the second at 4–6 years.[29]
In the UK, the National Health Service (NHS) recommendation is for a first dose at around 13 months of age and the second at three years and four months old.[30][31]
In Canada, Health Canada recommends that children traveling outside North America should receive an MMR vaccine if they are aged six to 12 months. However, after the child is 12 months old they should receive two additional doses to ensure long-lasting protection.[32]
Dosage
The defined daily dose is not established.[33]
Side effects
Side effects associated with the MMR vaccine include fever, rash, injection site pain and, in rare cases, red or purple discolorations on the skin known as thrombocytopenic purpura, or seizures related to fever (febrile seizure).[34][35]
Numerous studies have found no relationship between MMR vaccine and autism.[36][37][38][35]
Contraindications
Some people may not be able to receive the measles or MMR vaccine:
- Pregnancy: MMR vaccine and its components should not be given to pregnant women.[39] Women of childbearing age should check with their doctor about getting vaccinated prior to getting pregnant.[6]
- HIV-infected children may receive measles vaccines if their CD4+ lymphocyte count is greater than 15%.[40]
- Weakened immune systems due to HIV/AIDS or certain medical treatments[6]
- Parent or sibling with a history of immune problems [6]
- Condition that makes you bruise or bleed easily[6]
- Recently received a blood transfusion or other blood products[6]
- Have tuberculosis[6]
- Received other vaccines in the past 4 weeks[6]
- Not feeling well, even a mild illness such as a cold[6]
History
As a fellow at Children's Hospital Boston, Thomas C. Peebles worked with John Franklin Enders. Enders became known as "The Father of Modern vaccines", and Enders shared the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1954 for his research on cultivating the polio virus that led to the development of a vaccination for the disease.
Switching to study measles, Enders sent Peebles to Fay School in Massachusetts, where an outbreak of the disease was under way, and there Peebles was able to isolate the virus from some of the blood samples and throat swabs he had taken from the students. Even after Enders had taken him off the study team, Peebles was able to cultivate the virus and show that the disease could be passed on to monkeys inoculated with the material he had collected.[23] Enders was able to use the cultivated virus to develop a measles vaccine in 1963 based on the material isolated by Peebles.[41]
In the late 1950s and early 1960s, nearly twice as many children died from measles as from polio.[42] The vaccine Enders developed was based on the Edmonston strain of attenuated live measles virus, which was named for the 11-year-old David Edmonston, the Fay student from whom Peebles had taken the culture that led to the virus's cultivation.[43]
In the mid-20th century, measles was particularly devastating in West Africa, where child mortality rates were 50 percent before age 5, and the children were struck with the type of rash and other symptoms common prior to 1900 in England and other countries. The first trial of a live attenuated measles vaccine was undertaken in 1960 by the British paediatrician David Morley in a village near Ilesha, Nigeria; in case he could be accused of exploiting the Nigerian population, Morley included his own four children in the study. The encouraging results led to a second study of about 450 children in the village and at the Wesley Guild Hospital in Ilesha.
Following another epidemic, a larger trial was undertaken in September and October 1962, in New York City with the assistance of the World Health Organization (WHO): 131 children received the live Enders attenuated Edmonston B strain plus gamma globulin, 130 children received a "further attenuated" vaccine without gamma globulin, and 173 children acted as control subjects for both groups. As also shown in the Nigerian trial, the trial confirmed that the "further attenuated" vaccine was superior to the Edmonston B vaccine, and caused significantly fewer instances of fever and diarrhea. The successful results led to 2,000 children in the area being vaccinated.[44][45]
Maurice Hilleman at Merck & Co., a pioneer in the development of vaccinations, developed the MMR vaccine in 1971, which vaccinates against measles, mumps and rubella in a single shot followed by a booster.[24][46] One form is called "Attenuvax".[47] The measles component of the MMR vaccine uses Attenuvax,[48] which is grown in a chick embryo cell culture using the Enders' attenuated Edmonston strain.[48] Following ACIP recommendations, Merck decided not to resume production of Attenuvax as standalone vaccine on 21 October 2009.[49]
Types
Measles is seldom given as an individual vaccine and is often given in combination with rubella, mumps, or varicella (chickenpox) vaccines.[1] Below is the list of measles-containing vaccines:
- Measles vaccine (standalone vaccine)
- Measles and rubella combined vaccine (MR vaccine)
- Mumps, measles and rubella combined vaccine (MMR vaccine)[48][50][51]
- Mumps, measles, rubella and varicella combined vaccine (MMRV vaccine)[5]
Society and culture
Most health insurance plans in the United States cover the cost of vaccines, and Vaccines for Children Program may be able to help those who do not have coverage.[52] State law requires vaccinations for school children, but offer exemptions for medical reasons and sometimes for religious or philosophical reasons.[53] All fifty states require 2 doses of the MMR vaccine at the appropriate age.[54]
Cost
The wholesale cost in one country in the developing world, South Africa, is about 0.70 USD per dose as of 2015.[13]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 World Health Organization (April 2017). "Measles vaccines: WHO position paper – April 2017". Weekly Epidemiological Record. 92 (17): 205–27. hdl:10665/255377. PMID 28459148.
- Lay summary in: (PDF) https://www.who.int/immunization/policy/position_papers/WHO_PP_measles_vaccine_summary_2017.pdf?ua=1.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Missing or empty|title=(help)
- Lay summary in: (PDF) https://www.who.int/immunization/policy/position_papers/WHO_PP_measles_vaccine_summary_2017.pdf?ua=1.
- 1 2 3 "About Measles Vaccination | Vaccination and Immunizations | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 9 January 2020. Archived from the original on 27 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- 1 2 CDC (2 August 2019). "Measles and the Vaccine (Shot)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Archived from the original on 29 January 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ↑ Mitchell, Deborah (2013). The essential guide to children's vaccines. New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 127. ISBN 9781466827509. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- 1 2 "ProQuad- measles, mumps, rubella and varicella virus vaccine live injection, powder, lyophilized, for suspension". DailyMed. 26 September 2019. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "MMR Vaccination | What You Should Know | Measles, Mumps, Rubella | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 24 December 2019. Archived from the original on 26 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ↑ "Information Sheet Observed Rate of Vaccine Reactions" (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). Archived (PDF) from the original on 19 December 2019. Retrieved 1 December 2018.
- 1 2 "Measles History". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 February 2018. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Measles Fact sheet N°286". World Health Organization (WHO). November 2014. Archived from the original on 3 February 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ↑ "Immunization coverage". World Health Organization (WHO). Archived from the original on 13 July 2017. Retrieved 12 July 2017.
- 1 2 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2014). CDC health information for international travel 2014 the yellow book. p. 250. ISBN 9780199948505. Archived from the original on 8 September 2017.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- 1 2 "Vaccine, Measles". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 6 December 2015.
- ↑ Abramson, Brian (2018). Vaccine, vaccination, and immunization law. Bloomberg Law. pp. 10–30. ISBN 9781682675830.
- ↑ Babbott FL, Gordon JE (September 1954). "Modern measles". The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 228 (3): 334–61. doi:10.1097/00000441-195409000-00013. PMID 13197385.
- ↑ "Measles Prevention: Recommendations of the Immunization Practices Advisory Committee (ACIP)". www.cdc.gov. Archived from the original on 15 May 2012. Retrieved 27 April 2020.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (1994). "Summary of notifiable diseases, United States, 1993". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 42 (53): i–xvii, 1–73. PMID 9247368. Archived from the original on 9 March 2010.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (July 2007). "Summary of notifiable diseases, United States, 2007". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 56 (53): 1–94. Archived from the original on 13 June 2018. Retrieved 10 September 2017.
- ↑ Wallace G, Leroy Z (2015). "Measles". In Hamborsky J, Kroger A, Wolfe S (eds.). Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (13th ed.). Washington D.C.: Public Health Foundation. Archived from the original on 7 February 2015. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (help) - ↑ "Measles Cases and Outbreaks". Archived from the original on 13 February 2015. Retrieved 30 November 2018.
- ↑ Bloch AB, Orenstein WA, Stetler HC, Wassilak SG, Amler RW, Bart KJ, Kirby CD, Hinman AR (October 1985). "Health impact of measles vaccination in the United States". Pediatrics. 76 (4): 524–32. PMID 3931045.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (March 2006). "Progress in reducing global measles deaths, 1999-2004". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 55 (9): 247–9. PMID 16528234. Archived from the original on 16 October 2007.
- 1 2 Martin, Douglas (4 August 2010). "Dr. Thomas C. Peebles, Who Identified Measles Virus, Dies at 89". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 11 February 2017.
- 1 2 Collins, Huntly (30 August 1999). "The Man Who Saved Your Life - Maurice R. Hilleman - Developer of Vaccines for Mumps and Pandemic Flu". The Philadelphia Inquirer. Archived from the original on 6 March 2009. Retrieved 28 January 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 Parker AA, Staggs W, Dayan GH, Ortega-Sánchez IR, Rota PA, Lowe L, Boardman P, Teclaw R, Graves C, LeBaron CW (August 2006). "Implications of a 2005 measles outbreak in Indiana for sustained elimination of measles in the United States". The New England Journal of Medicine. 355 (5): 447–55. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa060775. PMID 16885548.
- ↑ Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (December 2006). "Measles--United States, 2005". MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 55 (50): 1348–51. PMID 17183226. Archived from the original on 13 March 2015.
- ↑ Sankoh O, Welaga P, Debpuur C, Zandoh C, Gyaase S, Poma MA, Mutua MK, Hanifi SM, Martins C, Nebie E, Kagoné M, Emina JB, Aaby P (June 2014). "The non-specific effects of vaccines and other childhood interventions: the contribution of INDEPTH Health and Demographic Surveillance Systems". International Journal of Epidemiology. 43 (3): 645–53. doi:10.1093/ije/dyu101. PMC 4052142. PMID 24920644.
- ↑ "Vaccine (Shot) for Measles". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 2 August 2019. Archived from the original on 29 January 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 "Birth-18 Years Immunization Schedule". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 5 February 2019. Archived from the original on 6 March 2016. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Measles". National Health Service UK. 20 October 2017. Archived from the original on 8 March 2019. Retrieved 11 March 2019.
- ↑ "MMR vaccine overview". National Health Service UK. 8 October 2019. Archived from the original on 31 January 2013. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ↑ "Measles vaccine: Canadian immunization guide". Public Health Agency of Canada. 18 July 2007. Archived from the original on 17 March 2019. Retrieved 13 March 2019.
- ↑ "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 24 September 2020. Retrieved 22 September 2020.
- ↑ "Information Sheet: Observed Rate of Vaccine Reactions: Measles, Mumps and Rubella Vaccines" (PDF). World Health Organization (WHO). May 2014. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 December 2019. Retrieved 1 December 2018.
- 1 2 Di Pietrantonj, Carlo; Rivetti, Alessandro; Marchione, Pasquale; Debalini, Maria Grazia; Demicheli, Vittorio (20 April 2020). "Vaccines for measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 4: CD004407. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004407.pub4. ISSN 1469-493X. PMC 7169657. PMID 32309885.
- ↑ "Measles, Mumps, and Rubella Vaccine". Adverse Effects of Vaccines: Evidence and Causality. Washington, D.C.: The National Academies Press. 9 April 2012. ISBN 978-0-309-21436-0. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 3 November 2017.
- ↑ "Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 22 August 2008. Archived from the original on 8 October 2008. Retrieved 21 December 2008.
- ↑ Institute of Medicine (US) Immunization Safety Review Committee (17 May 2004). Immunization Safety Review: Vaccines and Autism. Institute of Medicine of the National Academy of Sciences. doi:10.17226/10997. ISBN 978-0-309-09237-1. PMID 20669467. Archived from the original on 11 July 2007. Retrieved 19 October 2019.
- ↑ "Guidelines for Vaccinating Pregnant Women". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. August 2016. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
- ↑ "Contraindications and Precautions". Vaccine Recommendations and Guidelines of the ACIP. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 23 April 2020. Archived from the original on 1 May 2019. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
- ↑ "Work by Enders Brings Measles Vaccine License". The Hartford Courant. 22 March 1963. Archived from the original on 3 November 2012.
A strain of measles virus isolated in 1954 by Dr. Thomas C. Peebles, instructor in pediatrics at Harvard, and Enders, formed the basis for the development of the present vaccine
- ↑ "The Measles Vaccine". The New York Times. 28 March 1963. Archived from the original on 30 April 2019. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
- ↑ Hilleman MR (July 1992). "Past, present, and future of measles, mumps, and rubella virus vaccines". Pediatrics. 90 (1 Pt 2): 149–53. PMID 1603640.
- ↑ Morley DC, Woodland M, Krugman S, Friedman H, Grab B (1964). "Measles and Measles Vaccination in an African Village". Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 30: 733–9. PMC 2554995. PMID 14196817.
- ↑ Pritchard, John (13 November 1997). "Obituary: Dr C. A. Pearson". The Independent. Archived from the original on 24 February 2014. Retrieved 29 January 2014.
- ↑ Sullivan, Patricia (13 April 2005). "Maurice R. Hilleman Dies; Created Vaccines (washingtonpost.com)". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on 20 October 2012. Retrieved 21 July 2009.
- ↑ Ovsyannikova IG, Johnson KL, Naylor S, Poland GA (February 2005). "Identification of HLA-DRB1-bound self-peptides following measles virus infection". Journal of Immunological Methods. 297 (1–2): 153–67. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2004.12.020. PMID 15777939.
- 1 2 3 "M-M-R II- measles, mumps, and rubella virus vaccine live injection, powder, lyophilized, for suspension". DailyMed. 24 September 2019. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ↑ "Q&As about Monovalent M-M-R Vaccines". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 26 October 2009. Archived from the original on 19 October 2019. Retrieved 18 October 2019.
- ↑ "M-M-RVaxPro EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ↑ "Priorix - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 14 January 2020. Archived from the original on 6 April 2020. Retrieved 29 January 2020.
- ↑ "VFC | Home | Vaccines for Children Program | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 2 April 2019. Archived from the original on 1 May 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ↑ "State Vaccination Requirements | CDC". www.cdc.gov. 11 March 2019. Archived from the original on 2 April 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
- ↑ "MMR Vaccine Mandates for Child Care and K-12". www.immunize.org. Archived from the original on 12 June 2020. Retrieved 30 April 2020.
Further reading
- World Health Organization (2009). The immunological basis for immunization series : module 7: measles - Update 2009. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization (WHO). hdl:10665/44038. ISBN 9789241597555.
- Ramsay, Mary, ed. (2019). "Chapter 21: Measles". Immunisation against infectious disease. London, England: Public Health England. Archived from the original on 12 November 2019. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- Wallace G, Leroy Z (2015). "Chapter 13: Measles". In Hamborsky J, Kroger A, Wolfe S (eds.). Epidemiology and Prevention of Vaccine-Preventable Diseases (13th ed.). Washington D.C.: U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). ISBN 978-0990449119. Archived from the original on 30 December 2016. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- Gastanaduy PA, Redd SB, Clemmons NS, et al. (2019). "Chapter 7: Measles". In Roush SW, Baldy LM, Hall MH (eds.). Manual for the surveillance of vaccine-preventable diseases. Atlanta, Georgia: U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Archived from the original on 1 August 2020. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
External links
- "MMR (Measles, Mumps, & Rubella) Vaccine Information Statement". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 22 October 2019. Archived from the original on 3 September 2018. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- "MMRV (Measles, Mumps, Rubella & Varicella) Vaccine Information Statement". U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). 22 October 2019. Archived from the original on 26 December 2019. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- Measles Vaccine at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- "Measles Vaccine". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 24 October 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
| Identifiers: |
|---|
