Myoclonic astatic epilepsy
| Myoclonic astatic epilepsy | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Myoclonic-astatic epilepsy, myoclonic atonic epilepsy, Doose syndrome, epilepsy with myoclonic-atonic seizures, myoclonic-astatic epilepsy in early childhood | |
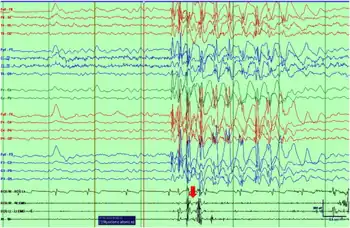 | |
| Ictal EEG with polygraphy of a myoclonic–atonic seizure shows initial myoclonus associated with the burst of polyspikes and atonia on the EMG associated with slow wave component of the discharge | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
Myoclonic astatic epilepsy (MAE), also known as myoclonic atonic epilepsy, is a generalized epilepsy of unknown cause. It is characterized by the development of myoclonic seizures or myoclonic astatic seizures.
Some of the common monogenic causes include mutations in the genes SLC6A1 (3p25.3),CHD2 (15q26.1), AP2M1 (10q23.2).[1]
Signs and symptoms
- Tonic-clonic seizures: seizures with repetitive sequences of stiffening and jerking of the extremities.
- Myoclonic seizures: seizures with rapid, brief contractions of muscles.
- Atonic seizures: seizures with a sudden loss of muscle tone, often resulting in sudden collapse. These are also called drop seizures or astatic seizures.
- Absence seizures: a generalized seizure characterized by staring off and occasionally some orofacial automatisms.
- Myoclonic astatic seizures: seizures that involve a myoclonic seizure followed immediately by an atonic seizure. This type of seizure is exclusive to MAE and is one of the defining characteristics of this syndrome.
- Tonic seizures: muscle stiffening or rigidity. This seizure is rare in this syndrome.
Onset
The onset of seizures is between the ages of 2 and 5 years of age. EEG shows regular and irregular bilaterally synchronous 2- to 3-Hz spike-waves and polyspike patterns with a 4- to 7-Hz background. 84% of affected children show normal development prior to seizures; the remainder show moderate psychomotor retardation mainly affecting speech. Boys (74%) are more often affected than girls (Doose and Baier 1987a).[2]
Diagnosis
The evaluation of Myoclonic–atonic seizure is done via the following:[3]
- Seizure semiology
- Neurologic examination
- Electroencephalogram findings
Treatments
The treatment for seizures may include antiepileptic medications, diet and vagus nerve stimulator.
Medication
Any number of medications may be used to both prevent and treat seizures.
Generally after three medications are tried, different treatment should be considered. Some medications are harmful to those with this syndrome and can increase seizures.
Diet
The ketogenic diet mimics some of the effects of starvation, in which the body first uses up glucose and glycogen before burning stored body fat. In the absence of glucose, the body produces ketones, a chemical by-product of fat metabolism that has been known to inhibit seizures.
A modified version of a popular low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet which is less restrictive than the ketogenic diet.
The low glycemic index treatment (LGIT) is a new dietary therapy currently being studied to treat epilepsy. LGIT attempts to reproduce the positive effects of the ketogenic diet. The treatment allows a more generous intake of carbohydrates than the ketogenic diet, but is restricted to foods that have a low glycemic index, meaning foods that have a relatively low impact on blood-glucose levels. These foods include meats, cheeses, and most vegetables because these foods have a relatively low glycemic index. Foods do not have to be weighed, but instead careful attention must be paid to portion size and balancing the intake of carbohydrates throughout the day with adequate amounts of fats and proteins.[4]
Prognosis
Epilepsy with myoclonic-astatic seizures has a variable course and outcome. Spontaneous remission with normal development has been observed in a few untreated cases. Complete seizure control can be achieved in about half of the cases with antiepileptic drug treatment (Doose and Baier 1987b; Dulac et al. 1990). In the remainder of cases, the level of intelligence deteriorates and the children become severely intellectually disabled. Other neurologic abnormalities such as ataxia, poor motor function, dysarthria, and poor language development may emerge (Doose 1992b). However, this proportion may not be representative because in this series the data were collected in an institution for children with severe epilepsy.
The outcome is unfavorable if generalized tonic-clonic, tonic, or clonic seizures appear at the onset or occur frequently during the course. Generalized tonic-clonic seizures usually occur during the daytime in this disorder, at least in the early stages. Nocturnal generalized tonic-clonic seizures, which may develop later, are another unfavorable sign. If tonic seizures appear, prognosis is poor.
Status epilepticus with myoclonic, astatic, myoclonic-astatic, or absence seizures is another ominous sign, especially when prolonged or appearing early.
Failure to suppress the EEG abnormalities (4- to 7-Hz rhythms and spike-wave discharges) during therapy and absence of occipital alpha-rhythm with therapy also suggest a poor prognosis (Doose 1992a).[2]
History
Myoclonic-astatic epilepsy was first described and identified in 1970 by Hermann Doose as an epilepsy syndrome, hence its original label, Doose syndrome.[5][6] 1989, it was classified as a symptomatic generalized epilepsy by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE).[5]
See also
References
- ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Myoclonic astatic epilepsy". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 2022-06-22. Retrieved 2022-08-14.
- 1 2 "Archive copy". Archived from the original on 2011-07-18. Retrieved 2022-08-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ RESERVED, INSERM US14-- ALL RIGHTS. "Orphanet: Myoclonic astatic epilepsy". www.orpha.net. Archived from the original on 22 June 2022. Retrieved 29 September 2022.
- ↑ "Low Glycemic Index Treatment (LGIT) | Comprehensive Epilepsy Center | NYU Medical Center, New York, NY". www.med.nyu.edu. Archived from the original on 2008-04-16.
- 1 2 Kelley, Sarah A; Kossof, Eric H (November 2010). "Doose syndrome (myoclonic-astatic epilepsy): 40 years of progress". Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology. 52 (11): 988–993. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2010.03744.x. PMID 20722665. S2CID 15674178.
- ↑ Delgado-Escueta, Antonio V. (2005). Myoclonic Epilepsies. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 147. ISBN 9780781752480. Archived from the original on 2022-09-30. Retrieved 2022-08-14.
External links
- Myoclonic astatic epilepsy at Curlie
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|