Thygeson's superficial punctate keratopathy
| Thygeson's superficial punctate keratopathy | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Thygeson Superficial Punctate Keratitis | |
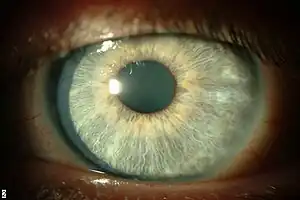 | |
| Full resolution of opacities. From Hasanreisoglu and Avisar, 2008.[1] | |
Thygeson's superficial punctate keratopathy (TSPK) is a disease of the eyes. The causes of TSPK are not currently known, but details of the disease were first published in the Journal of the American Medical Association in 1950 by renowned American ophthalmologist Phillips Thygeson (1903–2002), after whom it is named.[2]
Symptoms and signs
A patient with TSPK may complain of blurred vision, dry eyes, a sensation of having a foreign body stuck in the eye, photophobia (sensitivity to bright light), burning sensations and watery eyes. On inspection with a slit lamp, tiny lumps can be found on the cornea of the eye. These lumps can be more easily seen after applying fluorescein or rose Bengal dye eye-drops. The lumps appear to be randomly positioned on the cornea and they may appear and disappear over a period of time (with or without treatment).
TSPK may affect one or both eyes. When both eyes are affected, the tiny lumps found on the cornea may differ in number between eyes. The severity of the symptoms often vary during the course of the disease. The disease may appear to go into remission, only to later reappear after months or years.
Causes
The causes of TSPK are currently not yet well known.
Diagnosis
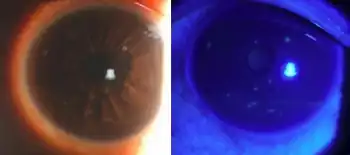
Differential diagnosis
The DDx is consistent with the following:[3]
- Pneumococcal conjunctivitis
- Seborrheic blepharitis
- Sjögren syndrome
- Exposure keratitis
Treatment
There are a number of different treatments to deal with TSPK. Symptoms may disappear if untreated, but treatment may decrease both the healing time and the chances of remission.
- Artificial tear eye-drops or ointments may be a suitable treatment for mild cases.
- Low-dosage steroidal eye-drops, such as prednisone, fluorometholone, loteprednol (Lotemax 0.5%) or rimexolone. Steroidal drops should be used with caution[4] and the eye pressure should be regularly checked during treatment.
- Soft contact lenses.
- Ciclosporin is an experimental treatment for TSPK. It is usually used during transplants as it reduces the immune system response.
- Tacrolimus (Protopic 0.03% ointment) is also an experimental treatment.
- Laser eye treatment.[5]
- Amniotic membrane (Case Study)[6]
- PRK laser eye surgery has been suggested in a one-person case study as having cured this disease.[7]
References
- ↑ Hasanreisoglu M, Avisar R (2008). "Long-term topical cyclosporin A therapy in Thygeson's superficial punctate keratitis: a case report". Cases J. 1 (1): 415. doi:10.1186/1757-1626-1-415. PMC 2636787. PMID 19105827.
- ↑ Thygeson P (December 1950). "Superficial punctate keratitis". J Am Med Assoc. 144 (18): 1544–9. doi:10.1001/jama.1950.02920180008004. PMID 14794375.
- ↑ "Thygeson Superficial Punctate Keratitis - EyeWiki". eyewiki.org. Archived from the original on 31 January 2022. Retrieved 24 August 2022.
- ↑ Tanzer DJ, Smith RE (1999). "Superficial punctate keratitis of thygeson: the longest course on record?". Cornea. 18 (6): 729–30. doi:10.1097/00003226-199911000-00017. PMID 10571306.
- ↑ Noble, Jason; Boerman, Helen; Jiang, Wei; Martén, Lisa; McCormick, Gregory J.; Pepose, Jay S.; Solomon, Renée; Yeu, Elizabeth; Peer-Reviewed Literature: The Treatment of Thygeson’s Superficial Punctate Keratitis, June 2007, Cataract & Refractive Surgery Today, pp. 21-23
- ↑ Kobayashi, Akira; Yoshita, Tsuyoshi; Sugiyama, Kazuhisa; Miyashita, Kengo; Niida, Yo; Koizumi, Shoichi; Tseng, Scheffer C.G. (January 2006). "Amniotic Membrane Transplantation in Acute Phase of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis with Severe Corneal Involvement". Ophthalmology. 113 (1): 126–132. doi:10.1016/j.ophtha.2005.09.001. PMID 16324747.
- ↑ Goldstein, Michael H.; Feistmann, Jonathan A.; Bhatti, M. Tariq (October 2002). "PRK-pTK as a treatment for a patient with Thygeson's superficial punctate keratopathy". The CLAO Journal. 28 (4): 172–173. ISSN 0733-8902. PMID 12394540. S2CID 23076934. Archived from the original on 2021-10-25. Retrieved 2022-03-16.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |