X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 13 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 324,313 times.
Learn more...
If you've decided that Ubuntu is no longer the right operating system for you, then you might be wondering how to go about deleting it from your system. Removing Ubuntu when it's the only operating system on your computer is fairly straightforward, but things get a little more complicated if you have Windows installed alongside it. Follow this guide to remove Ubuntu either way.
Steps
Method 1
Method 1 of 2:
Removing Ubuntu when Dual-Booting with Windows
-
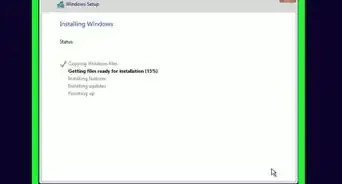
1Insert your Windows installation disc into your computer. This could also be labeled as a Recovery disc. If you don’t have an installation or recovery disc, you can create a recovery disc in Windows.
-
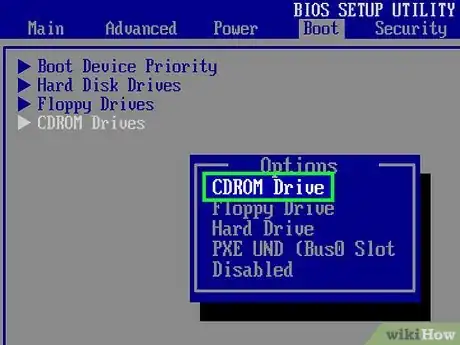
2Boot from the CD. In order to boot from your recovery disc, you’ll need to set your BIOS to boot from your CD/DVD drive. When the computer first starts up, press the BIOS setup key. This is typically F2, F10, F12, or Del. Navigate to the Boot menu and select your CD/DVD drive. Once you’ve selected it, save and reboot your computer.Advertisement
-
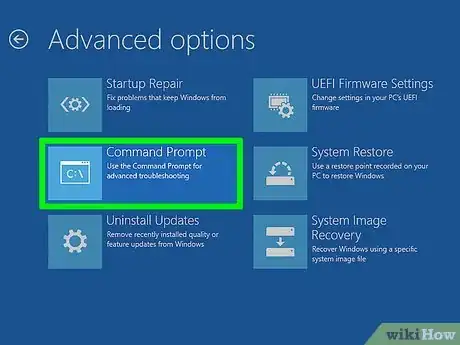
3Open the command prompt. From the Recovery Disc’s main menu, select the Command Prompt option. If you are using an Installation Disc, select “Repair your computer”, which should open the Command Prompt.
-
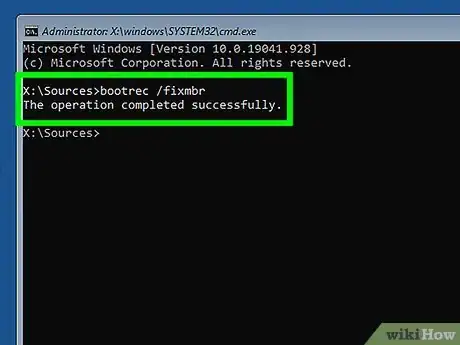
4Fix your Master Boot Record. Performing this command will remove the dual-boot option when you start your computer, and boot straight into Windows. Enter the following command at the Command Prompt:
bootrec /fixmbr -
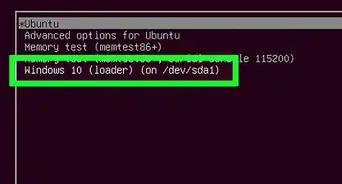
5Reboot your computer. When you reboot, you should not see the option to select Ubuntu. Instead, you will be taken directly into Windows.
-
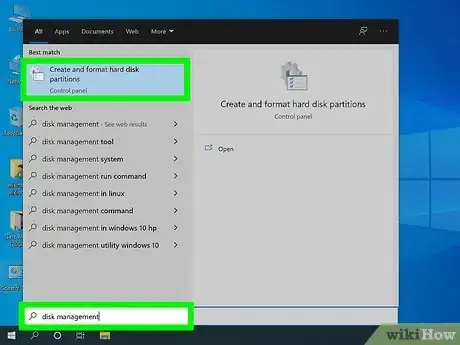
6Open Disk Management. Once in Windows, it’s time to get rid of the old Ubuntu installation and reclaim the hard disk space. Press Start, and the right-click on Computer/My Computer. Select Manage and then click Disk Management in the left frame of the Computer Management window.
- In Windows 8, press the Windows key + X and select Disk Management from the menu.
-
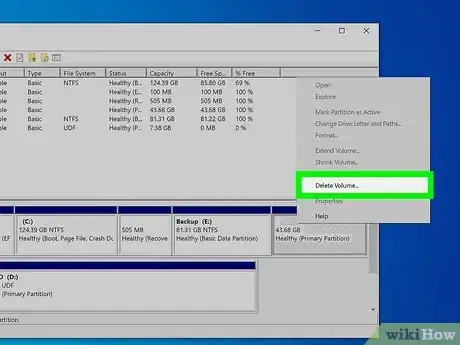
7Delete your Ubuntu partitions. Right-click on your Ubuntu partitions and select Delete. Make sure that you are deleting the correct partition. Once the partition is deleted, it will become unallocated space. Right-click on your Windows partition and select Extend partition. Select the free space just created to add it to your Windows installation.[1]
Advertisement
Method 2
Method 2 of 2:
Removing Ubuntu from a Single-Boot System
-
1Insert the disc of the operating system you want to install. When Ubuntu is the only operating system of the computer, you can remove it by using an operating system install disc for any operating system. Once you’ve inserted it, restart the computer and boot from CD, as outlined in Step 2 above.
-
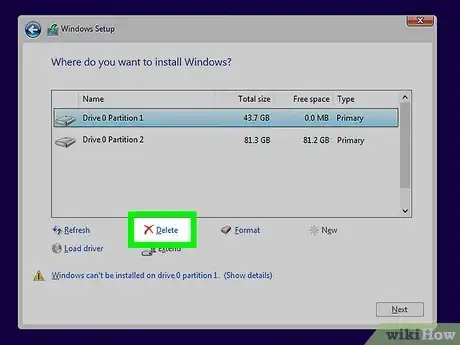
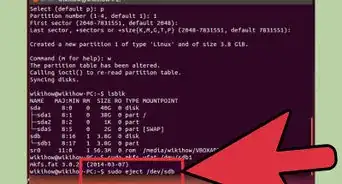
2Delete the Ubuntu partition. Once you start the installation process for the new operating system, you are given the opportunity to create and delete partitions on your hard drive. Select your Ubuntu partition and delete it. This will return the partition to unallocated space.
-
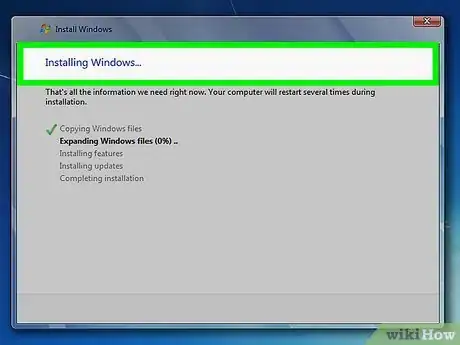
3Continue installing the operating system, or remove the disc and power down the computer. Once the partition is deleted, Ubuntu has been successfully removed from the computer. You can now install a new operating system such as Windows 7 or Windows 8.
- If you choose not to install the operating system, your computer will be unusable until one is installed.
Advertisement
Community Q&A
-
QuestionWhat is wrong if I don't see my partitions while installing Windows?
 Community AnswerThe Windows installer can't read the hard drive if this happens. You have to erase the drive using Gparted or the Ubuntu install media.
Community AnswerThe Windows installer can't read the hard drive if this happens. You have to erase the drive using Gparted or the Ubuntu install media. -
QuestionI can't do this. My Windows 10 is stuck and won't go past logo. Also when I insert a pen drive with the Windows installation media on it, the grub won't let me access the pen drive (USB). What do I do?
 Community AnswerBoot up a Ubuntu live CD install and go into try without installing, then when it has started up, go to parted, find the partition with Ubuntu on it and remove it, then reboot.
Community AnswerBoot up a Ubuntu live CD install and go into try without installing, then when it has started up, go to parted, find the partition with Ubuntu on it and remove it, then reboot.
Advertisement
About This Article
Advertisement