X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, volunteer authors worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 25,043 times.
Learn more...
Are you creating a website? Adding your own custom fonts on your webpage can make it more attractive and unique, compared to using the standard fonts. With the help of CSS, you can truly customize your webpage and help it stand out! This article includes an easy method you can use to apply your own fonts in HTML.
Steps
-
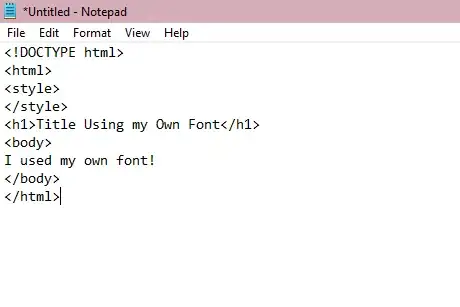
1Create a basic HTML webpage using any text editor tool. For example, you could be using Notepad, a free Windows system application. If you've already done this, you may skip this step.
- You should include the basic structure of an HTML document.
-
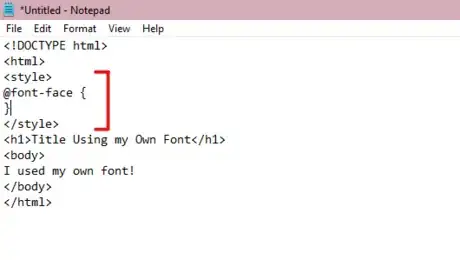
2Create a new font-face. Under your <style> tag, create a new font-family using the @font-face{} property. A font-face indicates that your font includes a font-family along with additional secondary attributes, for example, font-weight, bold, italic, thin, etc.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <style> @font-face { } </style> <h1>Title Using my Own Font</h1> <body> I used my own font! </body> </html>
Advertisement -
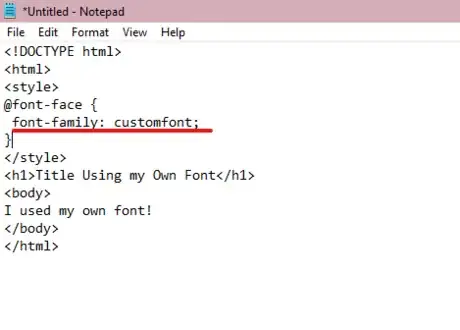
3Name your font. Use the font-family: property in between the parenthesis of the @font-face{} property. The font-family name indicates how you refer to it throughout your HTML document.
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <style> @font-face { font-family: customfont; } </style> <h1>Title Using my Own Font</h1> <body> I used my own font! </body> </html>
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
-
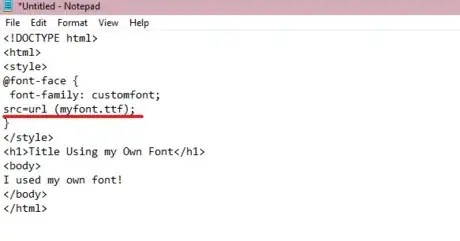
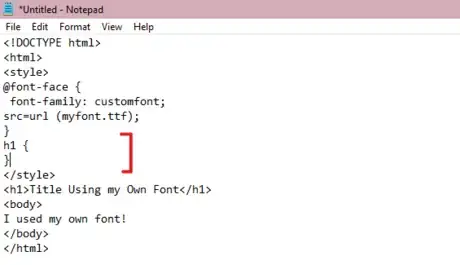
4Add your font file. Use the src=url () property in between the parenthesis of the @font-face{} property, mentioning the font file in between the parenthesis of the src=url () property.
- CSS accepts TTF, OTF, WOFF, SVG, and EOT font-file formats.
- Ensure your font file is saved in the same location as your HTML file, if not, specify the file's location. For example, /downloads/customfont.ttf.
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <style> @font-face { font-family: customfont; src=url (myfont.ttf); } </style> <h1>Title Using my Own Font</h1> <body> I used my own font! </body> </html>
-
5Edit your text. Create a new style attribute under the style tag, specifying which attribute you'd like to edit. For this example, we will be changing the title's font using h1 {}
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <style> @font-face { font-family: customfont; src=url (myfont.ttf); } h1 { } </style> <h1>Title Using my Own Font</h1> <body> I used my own font! </body> </html>
-
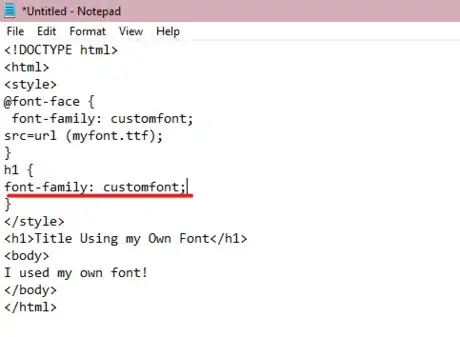
6Add your font to your text. Use the font-family: property under your newly created style property, specifying your font's name after the colon.
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <style> @font-face { font-family: customfont; src=url (myfont.ttf); } h1 { font-family: customfont; } </style> <h1>Title Using my Own Font</h1> <body> I used my own font! </body> </html>
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
-
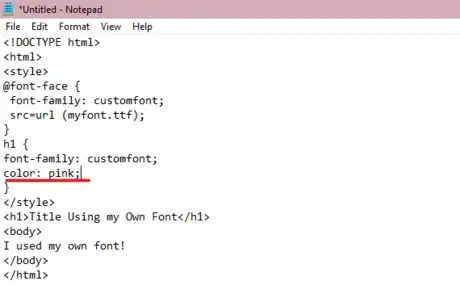
7Color your text. Use the color: property under your text's created style property, specifying your desired font's color after the colon.
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <style> @font-face { font-family: customfont; src=url (myfont.ttf); } h1 { font-family: customfont; color: pink; } </style> <h1>Title Using my Own Font</h1> <body> I used my own font! </body> </html>
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
-
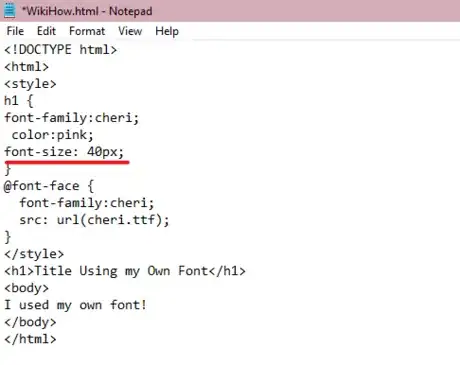
8Change your font size. Use the font-size: property under your text's created style property, specifying your desired font's size in pixels after the colon.
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <style> @font-face { font-family: customfont; src=url (myfont.ttf); } h1 { font-family: customfont; color: pink; font-size: 40px; } </style> <h1>Title Using my Own Font</h1> <body> I used my own font! </body> </html>
- A semicolon should be inserted after each property within a CSS style, indicating they're separated.
-
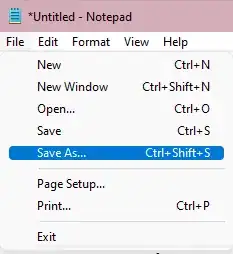
9Save your file using the .html extension. Press "File" and "Save as," name your file and ensure to add the .html towards the end. This step is important, as your file will only be considered a text file if you do not change the extension.
-
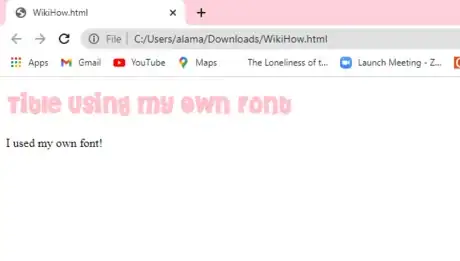
10Test your font. If done correctly, your text should now be displayed using your custom font. The location of the text depends on where you've applied the font.
Advertisement
Warnings
- If you're uploading a font to your website, ensure its free for commercial use first. Many custom fonts are generally only free for personal use, so if you're planning on actually hosting the website, it's best to either create your own font or look for fonts that can be used for free, commercially.⧼thumbs_response⧽
Advertisement
About This Article
Advertisement