EA-1356
EA-1356 is an organophosphate nerve agent of the G-series.[1][2] It is highly resistant to enzymatic degradation in the body. [3] The nerve agent was tested at Edgewood Arsenal in Maryland (the "EA" in "Ea-1356") among many other chemicals tested on humans. A novel enzyme was patented by the US Army in 2018 to break down EA-1356. It is a schedule 1 substance by the Chemical Weapons Convention standards. It is under the category of munitions of ML7.b.1.a.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
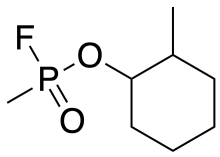
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Methylcyclohexyl methylphosphonofluoridate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H16FO2P | |
| Molar mass | 194.186 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Söderström MT, Ketola RA, Kostiainen O (1995). "Identification of some nerve agent homologues and dialkyl methylphosphonates by gas chromatography/Fourier transform infrared spectrometry". Fresenius' Journal of Analytical Chemistry. 352 (6): 550–556. doi:10.1007/BF00323072. S2CID 100910978.
- Ellison DH (2008). Handbook of Chemical and Biological Warfare Agents (Second ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-849-31434-6.
- US 10124043, Harvey SP, Guelta MA, McMahon LR, "Mutant OPAA enzymes with increased catalytic efficiency on organophosphorus compound EA1356", issued 13 November 2018, assigned to U.S. Army Edgewood Chemical Biological Center
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.