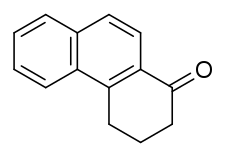
1-Keto-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrophenanthrene
1-Keto-1,2,3,4-tetrahydrophenanthrene (THP-1), or 1,2,3,4-tetrahydrophenanthren-1-one, is a synthetic steroid-like compound which was reported to be the first synthetic estrogen, or the first synthetic compound identified with estrogenic activity.[1][2] It was first synthesized in 1933 by Cook et al. and was tested due to its similarity to the presumed chemical structure of estrone.[1][2] Upon reassessment many decades later, the compound was found to bind only weakly to the estrogen receptors, and, unexpectedly, did not actually have functional activity as an estrogen or antiestrogen in vitro or in vivo.[2] It did, however, show some androgenic and antiandrogenic activity in vitro.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | THP-1; 1,2,3,4-Tetrahydrophenanthren-1-one |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H12O |
| Molar mass | 196.249 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
References
- Virgil Craig Jordan (1986). Estrogen/antiestrogen Action and Breast Cancer Therapy. Univ of Wisconsin Press. pp. 20–. ISBN 978-0-299-10480-1.
- Ashby J, Odum J, Paton D, Lefevre PA, Beresford N, Sumpter JP (2000). "Re-evaluation of the first synthetic estrogen, 1-keto-1,2,3, 4-tetrahydrophenanthrene, and bisphenol A, using both the ovariectomised rat model used in 1933 and additional assays". Toxicol. Lett. 115 (3): 231–8. doi:10.1016/s0378-4274(00)00198-3. PMID 10814893.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.