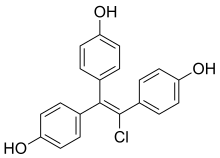
Desmethylchlorotrianisene
Desmethylchlorotrianisene (DMCTA) is a nonsteroidal estrogen which is thought to be the major active metabolite of chlorotrianisene (CTA; TACE).[1][2] It is a 1:1 mixture of cis and trans isomers.[1][2] DMCTA is produced from CTA via mono-O-demethylation catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver.[1][2] CTA is thought to act as a long-lasting prodrug of DMCTA.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | DMCTA |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal estrogen |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H15ClO3 |
| Molar mass | 338.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Ruenitz PC, Toledo MM (August 1981). "Chemical and biochemical characteristics of O-demethylation of chlorotrianisene in the rat". Biochem. Pharmacol. 30 (16): 2203–7. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(81)90088-5. PMID 7295335.
- Virgil Craig Jordan (1986). Estrogen/antiestrogen Action and Breast Cancer Therapy. Univ of Wisconsin Press. p. 212. ISBN 978-0-299-10480-1.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.