Ethylestradiol
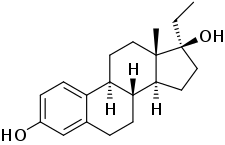
Ethylestradiol, or 17α-ethylestradiol, also known as 17α-ethylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol, is a synthetic estrogen which was never marketed. It occurs as an active metabolite of the anabolic steroids norethandrolone and ethylestrenol formed via aromatase and is believed to be responsible for the estrogenic effects of norethandrolone and ethylestrenol.[1] The 3-methyl ether of ethylestradiol has been used as an intermediate in the synthesis of certain 19-nortestosterone anabolic steroids.[2][3][4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 17α-Ethylestradiol; 17α-Ethylestra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol |
| Drug class | Estrogen |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H28O2 |
| Molar mass | 300.442 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
References
- Llewellyn W (2011). Anabolics. Molecular Nutrition Llc. pp. 330–, 591–598. ISBN 978-0-9828280-1-4.
- Colton FB, Nysted LN, Riegel B, Raymond AL (1957). "17-Alkyl-19-nortestosterones". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 79 (5): 1123–1127. doi:10.1021/ja01562a028. ISSN 0002-7863.
- Fedorova OI, Pekarskaya ES, Lukashina IV, Grinenko GS (1974). "Synthesis of some derivatives op 19-nortestosterone from estra-1,3,5(10)-trienes". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 8 (8): 462–465. doi:10.1007/BF00757882. ISSN 0091-150X. S2CID 27243268.
- William Andrew Publishing (22 October 2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. Elsevier. pp. 1513–. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.