Abrocitinib
Abrocitinib, sold under the brand name Cibinqo, is a Janus kinase inhibitor medication used for the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema).[3] It was developed by Pfizer.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Cibinqo |
| Other names | PF-04965842 |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 2.8–5.2 h |
| Excretion | 1.0–4.4% unchanged in urine |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.251.498 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
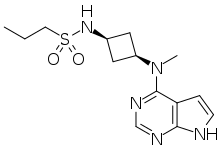
| Formula | C14H21N5O2S |
| Molar mass | 323.42 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Medical uses
Abrocitinib is indicated for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis in adults who are candidates for systemic therapy.[3]
Side effects
The most common adverse effects in studies were upper respiratory tract infection, headache, nausea, and diarrhea.[4]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
It is a selective inhibitor of the enzyme janus kinase 1 (JAK1).[4]
Pharmacokinetics
Abrocitinib is quickly absorbed from the gut and generally reaches highest blood plasma concentrations within one hour. Only 1.0 to 4.4% of the dose are found unmetabolized in the urine.[5]
History
Society and culture
Legal status
In October 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) of the European Medicines Agency (EMA) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Cibinqo, intended for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.[9] The applicant for this medicinal product is Pfizer Europe MA EEIG.[9] In December 2021, the European Commission approved abrocitinib for the treatment of atopic dermatitis.[3][10]
In January 2022, the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved abrocitinib for adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis.[11]
References
- "Cibinqo Product information". Health Canada. 25 April 2012. Retrieved 30 September 2022.
- "Cibinqo- abrocitinib tablet, film coated". DailyMed. 15 February 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- "Cibinqo EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 11 October 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- Gooderham MJ, Forman SB, Bissonnette R, Beebe JS, Zhang W, Banfield C, et al. (October 2019). "Efficacy and Safety of Oral Janus Kinase 1 Inhibitor Abrocitinib for Patients With Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial". JAMA Dermatology. 155 (12): 1371–1379. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.2855. PMC 6777226. PMID 31577341.
- Peeva E, Hodge MR, Kieras E, Vazquez ML, Goteti K, Tarabar SG, et al. (August 2018). "Evaluation of a Janus kinase 1 inhibitor, PF-04965842, in healthy subjects: A phase 1, randomized, placebo-controlled, dose-escalation study". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 84 (8): 1776–1788. doi:10.1111/bcp.13612. PMC 6046510. PMID 29672897.
- Clinical trial number NCT03349060 for "Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of PF-04965842 in Subjects Aged 12 Years And Older With Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis (JADE Mono-1)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- "Pfizer Presents Positive Phase 3 Data at the 28th Congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology for Abrocitinib in Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis". Drugs.com. 12 October 2019.
- Silverberg, J. I.; Simpson, E. L.; Thyssen, J. P.; Gooderham, M.; Chan, G.; Feeney, C.; Biswas, P.; Valdez, H.; Dibonaventura, M.; Nduaka, C.; Rojo, R. (3 June 2020). "Efficacy and Safety of Abrocitinib in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial". JAMA Dermatology. 156 (8): 863–873. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1406. PMC 7271424. PMID 32492087.
- "Cibinqo: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency. 15 October 2021. Retrieved 15 October 2021. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- "European Commission Approves Pfizer's Cibinqo (abrocitinib) for the Treatment of Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis". Pfizer Inc. (Press release). 10 December 2021. Retrieved 17 December 2021.
- "U.S. FDA Approves Pfizer's Cibinqo (abrocitinib) for Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis". Pfizer Inc. (Press release). 14 January 2022. Retrieved 16 January 2022.
External links
- "Abrocitinib". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Clinical trial number NCT03349060 for "Study to Evaluate Efficacy and Safety of PF-04965842 in Subjects Aged 12 Years And Older With Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis (JADE Mono-1)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03575871 for "Study Evaluating Efficacy and Safety of PF-04965842 in Subjects Aged 12 Years And Older With Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis (JADE Mono-2)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03720470 for "Study Evaluating Efficacy and Safety of PF-04965842 and Dupilumab in Adult Subjects With Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis on Background Topical Therapy (JADE Compare)" at ClinicalTrials.gov