Ripretinib
Ripretinib, sold under the brand name Qinlock, is a medication for the treatment of adults with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), a type of tumor that originates in the gastrointestinal tract.[3][4] It is taken by mouth.[3][4] Ripretinib inhibits the activity of the kinases KIT and PDGFRA, which helps keep cancer cells from growing.[4]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | rip re' ti nib |
| Trade names | Qinlock |
| Other names | DCC-2618 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a620035 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
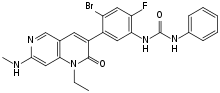
| Formula | C24H21BrFN5O2 |
| Molar mass | 510.367 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
The most common side effects include alopecia (hair loss), fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation, myalgia (muscle pain), diarrhea, decreased appetite, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (a skin reaction in the palms and soles) and vomiting.[4][5][6]
Ripretinib was approved for medical use in the United States in May 2020,[3][4] in Australia in July 2020,[1] and in the European Union in November 2021.[5] Ripretinib is the first new drug specifically approved in the United States as a fourth-line treatment for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST).
Medical uses
Ripretinib is indicated for the treatment of adults with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), a type of tumor that originates in the gastrointestinal tract, who have received prior treatment with three or more kinase inhibitor therapies, including imatinib.[3][4] GIST is type of stomach, bowel, or esophagus tumor.[6]
Adverse effects
The most common side effects include alopecia (hair loss), fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, constipation, myalgia (muscle pain), diarrhea, decreased appetite, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome (a skin reaction in the palms and soles) and vomiting.[4][6]
Ripretinib can also cause serious side effects including skin cancer, hypertension (high blood pressure) and cardiac dysfunction manifested as ejection fraction decrease (when the muscle of the left ventricle of the heart is not pumping as well as normal).[4][6]
Ripretinib may cause harm to a developing fetus or a newborn baby.[4][6]
History
Ripretinib was approved for medical use in the United States in May 2020.[4][7][8][6]
The approval of ripretinib was based on the results of an international, multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (INVICTUS/NCT03353753) that enrolled 129 participants with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST) who had received prior treatment with imatinib, sunitinib, and regorafenib.[4][9] The trial compared participants who were randomized to receive ripretinib to participants who were randomized to receive placebo, to determine whether progression free survival (PFS) – the time from initial treatment in the clinical trial to growth of the cancer or death – was longer in the ripretinib group compared to the placebo group.[4] During treatment in the trial, participants received ripretinib 150 mg or placebo once a day in 28-day cycles, repeated until tumor growth was found (disease progression), or the participant experienced intolerable side effects.[4][9] After disease progression, participants who were randomized to placebo were given the option of switching to ripretinib.[4][9] The trial was conducted at 29 sites in the United States, Australia, Belgium, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, Poland, Singapore, Spain, and the United Kingdom.[6]
The major efficacy outcome measure was progression-free survival (PFS) based on assessment by blinded independent central review (BICR) using modified RECIST 1.1 in which lymph nodes and bone lesions were not target lesions and a progressively growing new tumor nodule within a pre-existing tumor mass must meet specific criteria to be considered unequivocal evidence of progression.[9] Additional efficacy outcome measures included overall response rate (ORR) by BICR and overall survival (OS).[9] The trial demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in PFS for participants in the ripretinib arm compared with those in the placebo arm (HR 0.15; 95% CI: 0.09, 0.25; p<0.0001).[9]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted the application for ripretinib priority review and fast track designations, as well as breakthrough therapy designation and orphan drug designation.[4][10] The FDA granted approval of Qinlock to Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Inc.[4]
Society and culture
Legal status
Ripretinib was approved for medical use in the United States in May 2020,[4] and in Australia in July 2020.[1]
On 16 September 2021, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of a marketing authorization for the medicinal product Qinlock, intended for the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumour (GIST) in people who have received prior treatment with three or more kinase inhibitors.[11] The applicant for this medicinal product is Deciphera Pharmaceuticals (Netherlands) B.V.[11] Ripretinib was approved for medical use in the European Union in November 2021.[5]
Names
Ripretinib is the International nonproprietary name (INN) and the United States Adopted Name (USAN).[12][13]
References
- "Qinlock Australian Prescription Medicine Decision Summary". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 21 July 2020. Retrieved 17 August 2020.
- "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Qinlock". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- "Qinlock- ripretinib tablet". DailyMed. Retrieved 13 February 2022.
- "FDA Approves First Drug for Fourth-Line Treatment of Advanced Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Qinlock EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). 14 September 2021. Retrieved 13 February 2022.
- "Drug Trial Snapshot: Qinlock". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 2 June 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "FDA Grants Full Approval of Deciphera Pharmaceuticals' Qinlock (ripretinib) for the Treatment of Fourth-Line Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor". Deciphera Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Press release). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- "Qinlock: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- "FDA approves ripretinib for advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumor". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 15 May 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - "Ripretinib Orphan Drug Designation and Approval". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2 October 2014. Retrieved 15 May 2020.
- "Qinlock: Pending EC decision". European Medicines Agency. 16 September 2021. Retrieved 17 September 2021. Text was copied from this source which is © European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- World Health Organization (2019). "International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 81". WHO Drug Information. 33 (1): 106. hdl:10665/330896. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- "Ripretinib" (PDF). United States Adopted Name (USAN) Drug Finder. Retrieved 17 May 2020.
Further reading
- Schneeweiss M, Peter B, Bibi S, et al. (May 2018). "The KIT and PDGFRA switch-control inhibitor DCC-2618 blocks growth and survival of multiple neoplastic cell types in advanced mastocytosis". Haematologica. 103 (5): 799–809. doi:10.3324/haematol.2017.179895. PMC 5927976. PMID 29439183.
External links
- "Ripretinib". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Ripretinib". NCI Drug Dictionary. National Cancer Institute.
- "Ripretinib". National Cancer Institute. 27 May 2020.
- Clinical trial number NCT03353753 for "Phase 3 Study of DCC-2618 vs Placebo in Advanced GIST Patients Who Have Been Treated With Prior Anticancer Therapies (invictus)" at ClinicalTrials.gov