Bosutinib
Bosutinib (rINN/USAN; codenamed SKI-606, marketed under the trade name Bosulif) is a small molecule BCR-ABL and src tyrosine kinase inhibitor used for the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia.
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bosulif |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 94–96% |
| Metabolism | By CYP3A4, to inactive metabolites |
| Elimination half-life | 22.5±1.7 hours |
| Excretion | Foecal (91.3%) and renal (3%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.122 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
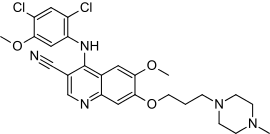
| Formula | C26H29Cl2N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 530.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Originally synthesized by Wyeth, it is being developed by Pfizer.
Mechanism
It is an ATP-competitive Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitor with an additional inhibitory effect on Src family kinases (including Src, Lyn and Hck).[1][2] It has also shown activity against the receptors for platelet derived growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor.[3] Bosutinib inhibited 16 of 18 imatinib-resistant forms of Bcr-Abl expressed in murine myeloid cell lines, but did not inhibit T315I and V299L mutant cells.[1]
Bosutinib is metabolized through CYP3A4.
Medical uses
Bosutinib received US FDA and EU European Medicines Agency approval in September 2012, and March 2013, respectively for the treatment of adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) with resistance, or intolerance to prior therapy.[4][5][6][7]
Contraindications
Bosutinib has two known absolute contraindications, which are: known hypersensitivity to bosutinib and liver impairment.[8][9]
Interactions
Bosutinib is both a substrate and an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and CYP3A4.[1] Hence P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase plasma levels of bosutinib.[1] Likewise CYP3A4 inducers may reduce plasma concentrations of bosutinib.[1] It may also alter the metabolism and uptake (into the GIT by means of its P-gp inhibitory effects) of other drugs that are substrates for P-gp and CYP3A4.[1]

Notes
References
- "Bosulif (bosutinib) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- Daud AI, Krishnamurthi SS, Saleh MN, Gitlitz BJ, Borad MJ, Gold PJ, et al. (February 2012). "Phase I study of bosutinib, a src/abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor, administered to patients with advanced solid tumors". Clinical Cancer Research. 18 (4): 1092–100. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2378. PMID 22179664.
- Bosutinib. livertox.nih.gov. 2012.
- Cortes JE, Kantarjian HM, Brümmendorf TH, Kim DW, Turkina AG, Shen ZX, et al. (October 2011). "Safety and efficacy of bosutinib (SKI-606) in chronic phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to imatinib". Blood. 118 (17): 4567–76. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-05-355594. PMC 4916618. PMID 21865346.
- Cortes JE, Kim DW, Kantarjian HM, Brümmendorf TH, Dyagil I, Griskevicius L, et al. (October 2012). "Bosutinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results from the BELA trial". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 30 (28): 3486–92. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.7522. PMC 4979199. PMID 22949154.
- "Bosulif Approved for Previously Treated Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia". 5 September 2012.
- "Bosulif : EPAR - Product Information" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Pfitzer Ltd. 9 April 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- "Bosulif 100mg and 500mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium. Pfitzer Limited. 7 June 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- "BOSULIF (bosutinib monohydrate) tablet, film coated [Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc]". DailyMed. Pfitzer Inc. September 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
External links
- "Bosutinib". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.