Momelotinib
Momelotinib (INN,[1] formerly GS-0387, CYT-387) is an inhibitor of Janus kinases JAK1 and JAK2, acting as an ATP competitor with IC50 values of 11 and 18 nM, respectively. The inhibitor is significantly less active towards other kinases, including JAK3 (IC50 = 0.16 μM).[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
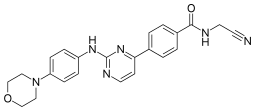
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-(Cyanomethyl)-4-{2-[4-(morpholin-4-yl)anilino]pyrimidin-4-yl}benzamide | |
| Other names
CYT-387, CYT-11387, GS-0387 | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C23H22N6O2 |
| Molar mass | 414.469 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
As of 2011, momelotinib is being developed as a drug for myelofibrosis and currently undergoes Phase I/II clinical trials. Additional potential treatment indications for momelotinib include other myeloproliferative neoplasms, cancer (solid and liquid tumors) and inflammatory conditions.[3]
As of 2016, momelotinib is being investigated for primary myelofibrosis or post-polycythemia vera or post-essential thrombocythemia myelofibrosis (post-PV/ET MF),[4] as well as a treatment for relapsed or refractory metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (in combination with capecitabine and oxaliplatin).[5]
Discovery
The drug was originally discovered by Australian drug discovery company Cytopia, then developed by YM BioSciences Inc. (since acquired by Gilead Sciences as of 2013).
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Proposed International Nonproprietary Names: List 107" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 189. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- Pardanani, A; Lasho, T; Smith, G; Burns, CJ; Fantino, E; Tefferi, A (August 2009). "CYT387, a Selective JAK1/JAK2 Inhibitor: in vitro Assessment of Kinase Selectivity and Preclinical Studies Using Cell Lines and Primary Cells from Polycythemia vera Patients" (PDF). Leukemia. 23 (8): 1441–5. doi:10.1038/leu.2009.50. PMID 19295546. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- Pardanani, A; Vannucchi, AM; Passamonti, F; Cervantes, F; Barbui, T; Tefferi, A (February 2011). "JAK Inhibitor Therapy for Myelofibrosis: Critical Assessment of Value and Limitations" (PDF). Leukemia. 25 (2): 218–25. doi:10.1038/leu.2010.269. PMID 21079613. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- "Momelotinib in Transfusion-Dependent Adults with Primary Myelofibrosis (PMF) or Post-polycythemia Vera or Post-essential Thrombocythemia Myelofibrosis (Post-PV/ET MF)". ClinicalTrials.gov. Retrieved 16 July 2016.
- "Momelotinib Combined with Capecitabine and Oxaliplatin in Adults with Relapsed/Refractory Metastatic Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma". ClinicalTrials.gov. Retrieved 16 July 2016.