Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is a viral infectious disease involving the central nervous system. The disease most often manifests as meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Myelitis and spinal paralysis also occurs. In about one third of cases sequelae, predominantly cognitive dysfunction, persists for a year or more.[1]
| Tick-borne meningoencephalitis | |
|---|---|
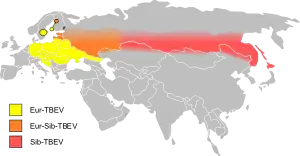 | |
| Infected countries/areas in Eurasia | |
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
The number of reported cases has been increasing in most countries.[2] TBE is posing a concerning health challenge to Europe, as the number of reported human cases of TBE in all endemic regions of Europe have increased by almost 400% within the last three decades.[3]
The tick-borne encephalitis virus is known to infect a range of hosts including ruminants, birds, rodents, carnivores, horses, and humans. The disease can also be spread from animals to humans, with ruminants and dogs providing the principal source of infection for humans.[4]
Signs and symptoms
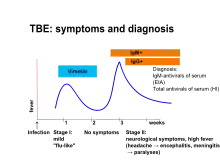
The disease is most often biphasic. After an incubation period of approximately one week (range: 4–28 days) from exposure (tick bite) non-specific symptoms occurs. These symptoms are fever, malaise, headache, nausea, vomiting and myalgias that persist for about 5 days.[1][3][5] Then, after approximately one week without symptoms, some of the infected develop neurological symptoms, i.e. meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis. Myelitis also occurs with or without encephalitis.[1][3][5][6]
Sequelae persists for a year or more in approximately one third of people who develop neurological disease. Most common long-term symptoms are headache, concentration difficulties, memory impairment and other symptoms of cognitive dysfunction.[1]
Mortality depends on the subtype of the virus. For the European subtype mortality rates are 0.5% to 2% for people who develop neurological disease.[3]
In dogs, the disease also manifests as a neurological disorder with signs varying from tremors to seizures and death.[4]
In ruminants, neurological disease is also present, and animals may refuse to eat, appear lethargic, and also develop respiratory signs.[4]
Cause
TBE is caused by tick-borne encephalitis virus, a member of the genus Flavivirus in the family Flaviviridae. It was first isolated in 1937. Three virus sub-types also exist: European or Western tick-borne encephalitis virus (transmitted by Ixodes ricinus), Siberian tick-borne encephalitis virus (transmitted by I. persulcatus), and Far-Eastern tick-borne encephalitis virus, formerly known as Russian spring summer encephalitis virus (transmitted by I. persulcatus).[3][7]
The former Soviet Union conducted research on tick-borne diseases, including the TBE viruses.
Transmission

It is transmitted by the bite of several species of infected woodland ticks, including Ixodes scapularis, I. ricinus and I. persulcatus,[8] or (rarely) through the non-pasteurized milk of infected cows.[9]
Infection acquired through goat milk consumed as raw milk or raw cheese (Frischkäse) has been documented in 2016 and 2017 in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. None of the infected had neurological disease.[10]
Diagnosis
Detection of specific IgM and IgG antibodies in patients sera combined with typical clinical signs, is the principal method for diagnosis. In more complicated situations, e.g. after vaccination, testing for presence of antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid may be necessary.[3] It has been stated that lumbar puncture always should be performed when diagnosing TBE and that pleocytosis in cerebrospinal fluid should be added to the diagnostic criteria.[11]
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method is rarely used, since TBE virus RNA is most often not present in patient sera or cerebrospinal fluid at the time of neurological symptoms.[11]
Prevention

Prevention includes non-specific (tick-bite prevention, tick checks) and specific prophylaxis in the form of a vaccination. Tick-borne encephalitis vaccines are very effective and available in many disease endemic areas and in travel clinics.[12] Trade names are Encepur N[13] and FSME-Immun CC.[14]
Treatment
There is no specific antiviral treatment for TBE. Symptomatic brain damage requires hospitalization and supportive care based on syndrome severity. Anti-inflammatory drugs, such as corticosteroids, may be considered under specific circumstances for symptomatic relief. Tracheal intubation and respiratory support may be necessary.
Epidemiology
As of 2011, the disease was most common in Central and Eastern Europe, and Northern Asia. About ten to twelve thousand cases are documented a year but the rates vary widely from one region to another.[15] Most of the variation has been the result of variation in host population, particularly that of deer. In Austria, an extensive vaccination program since the 1970s reduced the incidence in 2013 by roughly 85%.[16]
In Germany, during the 2010s, there have been a minimum of 95 (2012) and a maximum of 584 cases (2018) of TBE (or FSME as it is known in German). More than half of the reported cases from 2019 had meningitis, encephalitis or myelitis. The risk of infection was noted to be increasing with age, especially in people older than 40 years and it was greater in men than women. Most cases were acquired in Bavaria (46%) and Baden-Württemberg (37%), much less in Saxony, Hesse, Lower Saxony and other states. Altogether 164 Landkreise are designated TBE-risk areas, including all of Baden-Württemberg except for the city of Heilbronn.[10]
In Sweden, most cases of TBE occur in a band running from Stockholm to the west, especially around lakes and the nearby region of the Baltic sea.[17][18] It reflects the greater population involved in outdoor activities in these areas. Overall, for Europe, the estimated risk is roughly 1 case per 10,000 human-months of woodland activity. Although in some regions of Russia and Slovenia, the prevalence of cases can be as high as 70 cases per 100,000 people per year.[16][19] Travelers to endemic regions do not often become cases, with only 5 cases reported among U.S. travelers returning from Eurasia between 2000 and 2011, a rate so low that as of 2016 the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended vaccination only for those who will be extensively exposed in high risk areas.[20]
References
- Lindquist, Lars; Vapalahti, Olli (2008-05-31). "Tick-borne encephalitis". The Lancet. 371 (9627): 1861–1871. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60800-4. ISSN 0140-6736. PMID 18514730. S2CID 901857.
- Suss J (June 2008). "Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe and beyond--the epidemiological situation as of 2007". Euro Surveill. 13 (26). doi:10.2807/ese.13.26.18916-en. PMID 18761916.
- "Factsheet about tick-borne encephalitis (TBE)". European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- Tickborne Encephalitis Virus reviewed and published by WikiVet, accessed 12 October 2011.
- Riccardi N (22 January 2019). "Tick-borne encephalitis in Europe: a brief update on epidemiology, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment". Eur J Intern Med. 62: 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2019.01.004. PMID 30678880. S2CID 59252822.
- Kaiser R (September 2008). "Tick-borne encephalitis". Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 22 (3): 561–75, x. doi:10.1016/j.idc.2008.03.013. PMID 18755391.
- "Tick-borne Encephalitis (TBE)". Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved 15 January 2019.
- Dumpis U, Crook D, Oksi J (April 1999). "Tick-borne encephalitis". Clin. Infect. Dis. 28 (4): 882–90. doi:10.1086/515195. PMID 10825054.
- CDC Yellow Book, accessed 5 October 2013.
- "FSME: Risikogebiete in Deutschland" (PDF). Epidemiologisches Bulletin, RKI (in German). Berlin. 8. 2020.
- Taba, P.; Schmutzhard, E.; Forsberg, P.; Lutsar, I.; Ljøstad, U.; Mygland, Å.; Levchenko, I.; Strle, F.; Steiner, I. (October 2017). "EAN consensus review on prevention, diagnosis and management of tick-borne encephalitis". European Journal of Neurology. 24 (10): 1214–e61. doi:10.1111/ene.13356. PMID 28762591. S2CID 12844392.
- Demicheli V, Debalini MG, Rivetti A (2009). Demicheli V (ed.). "Vaccines for preventing tick-borne encephalitis". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1): CD000977. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000977.pub2. PMC 6532705. PMID 19160184.
- "Encepur® N". compendium.ch. 2016-04-28. Retrieved 2018-01-21.
- "FSME-Immun® CC". compendium.ch. 2017-08-11. Retrieved 2018-01-21.
- "Vaccines against tick-borne encephalitis: WHO position paper" (PDF). Relevé Épidémiologique Hebdomadaire. 86 (24): 241–56. 10 June 2011. PMID 21661276.
- Amicizia, Daniela; Domnich, Alexander; Panatto, Donatella; Lai, Piero Luigi; Cristina, Maria Luisa; Avio, Ulderico; Gasparini, Roberto (2013-05-14). "Epidemiology of tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) in Europe and its prevention by available vaccines". Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics. 9 (5): 1163–1171. doi:10.4161/hv.23802. ISSN 2164-5515. PMC 3899155. PMID 23377671.
- Pettersson, John H.-O.; Golovljova, Irina; Vene, Sirkka; Jaenson, Thomas G. T. (2014-01-01). "Prevalence of tick-borne encephalitis virus in Ixodes ricinus ticks in northern Europe with particular reference to Southern Sweden". Parasites & Vectors. 7: 102. doi:10.1186/1756-3305-7-102. ISSN 1756-3305. PMC 4007564. PMID 24618209.
- team, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC)-Health Communication Unit- Eurosurveillance editorial (2011). "Tick-borne encephalitis increasing in Sweden, 2011". Eurosurveillance. 16 (39). doi:10.2807/ese.16.39.19981-en. PMID 21968422.
- team, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC)-Health Communication Unit- Eurosurveillance editorial (2011-03-11). "Case report: Tick-borne encephalitis in two Dutch travellers returning from Austria, Netherlands, July and August 2011". Eurosurveillance. 16 (44): 20003. doi:10.2807/ese.16.44.20003-en. PMID 22085619. Retrieved 2016-06-04.
- "Tickborne Encephalitis - Chapter 3 - 2016 Yellow Book | Travelers' Health | CDC". wwwnc.cdc.gov. Retrieved 2016-06-04.
External links
- Tickborne encephalitis at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Factsheet from Viral Special Pathogens Branch at the CDC