IDX-184
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
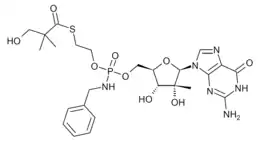
| Formula | C25H35N6O9PS |
| Molar mass | 626.6 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
IDX-184 is an antiviral drug which was developed as a treatment for hepatitis C, acting as a NS5B RNA polymerase inhibitor.[1][2] While it showed reasonable effectiveness in early clinical trials it did not progress past Phase IIb.[3] However research using this drug has continued as it shows potentially useful activity against other emerging viral diseases such as Zika virus,[4][5] and coronaviruses including MERS,[6] and SARS-CoV-2.[7][8]
References
- ↑ Elfiky AA, Elshemey WM (2016). "IDX-184 is a superior HCV direct-acting antiviral drug: a QSAR study". Medicinal Chemistry Research. 25 (5): 1005–1008. doi:10.1007/s00044-016-1533-y. PMC 7080126. PMID 32214769.
- ↑ Elfiky AA (2019). "Novel Guanosine Derivatives as Anti-HCV NS5b Polymerase: A QSAR and Molecular Docking Study". Medicinal Chemistry. 15 (2): 130–137. doi:10.2174/1573406414666181015152511. PMID 30324891.
- ↑ Gentile I, Buonomo AR, Zappulo E, Borgia G (February 2015). "Discontinued drugs in 2012 - 2013: hepatitis C virus infection". Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs. 24 (2): 239–51. doi:10.1517/13543784.2015.982274. PMID 25384989. S2CID 39936873.
- ↑ Elfiky AA (December 2016). "Zika viral polymerase inhibition using anti-HCV drugs both in market and under clinical trials". Journal of Medical Virology. 88 (12): 2044–2051. doi:10.1002/jmv.24678. PMID 27604059. S2CID 21846603.
- ↑ Elfiky AA, Ismail AM (May 2018). "Molecular docking revealed the binding of nucleotide/side inhibitors to Zika viral polymerase solved structures". SAR and QSAR in Environmental Research. 29 (5): 409–418. doi:10.1080/1062936X.2018.1454981. PMID 29652194. S2CID 4811956.
- ↑ Elfiky AA, Mahdy SM, Elshemey WM (June 2017). "Quantitative structure-activity relationship and molecular docking revealed a potency of anti-hepatitis C virus drugs against human corona viruses". Journal of Medical Virology. 89 (6): 1040–1047. doi:10.1002/jmv.24736. PMC 7167072. PMID 27864902.
- ↑ Elfiky AA (May 2020). "Anti-HCV, nucleotide inhibitors, repurposing against COVID-19". Life Sciences. 248: 117477. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117477. PMC 7089605. PMID 32119961.
- ↑ Elfiky AA (March 2020). "Ribavirin, Remdesivir, Sofosbuvir, Galidesivir, and Tenofovir against SARS-CoV-2 RNA dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp): A molecular docking study". Life Sciences. 253: 117592. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117592. PMC 7102646. PMID 32222463.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.