Omidenepag
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Eybelis, Omlonti |
| Other names | UR-7276, DE-117, Omidenepag isopropyl (JAN JP) |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Prostaglandin E2 (EP2) receptor activator[1] |
| Main uses | Ocular hypertension including glaucoma[1] |
| Side effects | Sensitivity to light, blurry vision, eye redness, headache, eye pain[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Routes of use | Eye drop |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
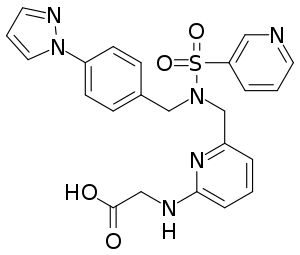
| Formula | C26H28N6O4S |
| Molar mass | 520.61 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Omidenepag, sold under the brand name Eybelis among others, is a medication used to treat ocular hypertension including glaucoma.[1][3] It is used as an eye drop.[1]
Common side effects include sensitivity to light, blurry vision, eye redness, headache, and eye pain.[1] Other side effects may include changes to the eyelashes and macular edema.[1] It is a relatively selective prostaglandin E2 (EP2) receptor activator.[1]
Omidenepag was approved for medical use in Japan in 2018,[3] and the United States in 2022.[1] It is not currently in the approval process in either Europe or the United Kingdom as of 2022.[4]
Medical uses
Omidenepag is indicated for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension.[1][3]
Dosage
It comes as a 0.002% (0.02 mg/mL) solution.[1] It is used as one drop once per day.[1]
Side effects
The most common side effects are conjunctival hyperemia and macular edema, including cystoid macular edema.[3]
Pharmacology
Omidenepag isopropyl is a prodrug that is converted by hydrolysis of its isopropyl ester to the active metabolite omidenepag.[5] Omidenepag is a selective prostaglandin E2 receptor agonist.[6][7]
History
Omidenepag was developed by Ube Industries and Santen Pharmaceutical.[3]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Omlonti- omidenepag isopropyl solution/ drops". DailyMed. 30 September 2022. Archived from the original on 16 October 2022. Retrieved 16 October 2022.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Omlonti". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 October 2022. Archived from the original on 4 December 2022. Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Duggan S (December 2018). "Omidenepag Isopropyl Ophthalmic Solution 0.002%: First Global Approval". Drugs. 78 (18): 1925–1929. doi:10.1007/s40265-018-1016-1. PMID 30465134. S2CID 53721056.
- ↑ "Omidenepag isopropyl". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 30 September 2022. Archived from the original on 24 October 2022. Retrieved 16 December 2022.
- ↑ "Omidenepag isopropyl". DrugCentral. Division of Translational Informatics at University of New Mexico. Archived from the original on 8 January 2022. Retrieved 8 January 2022.
- ↑ Kirihara T, Taniguchi T, Yamamura K, Iwamura R, Yoneda K, Odani-Kawabata N, et al. (January 2018). "Pharmacologic Characterization of Omidenepag Isopropyl, a Novel Selective EP2 Receptor Agonist, as an Ocular Hypotensive Agent". Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science. 59 (1): 145–153. doi:10.1167/iovs.17-22745. PMID 29332128.
- ↑ Ida Y, Hikage F, Umetsu A, Ida H, Ohguro H (September 2020). "Omidenepag, a non-prostanoid EP2 receptor agonist, induces enlargement of the 3D organoid of 3T3-L1 cells". Scientific Reports. 10 (1): 16018. Bibcode:2020NatSR..1016018I. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-72538-x. PMC 7524797. PMID 32994409.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- "Omidenepag isopropyl". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2022-10-02. Retrieved 2022-12-04.
- "Omidenepag". NCI Thesaurus. Archived from the original on 2022-10-07. Retrieved 2022-12-04.
- "Omidenepag isopropyl". NCI Thesaurus. Archived from the original on 2022-10-07. Retrieved 2022-12-04.