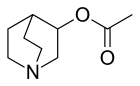
Aceclidine
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Topical (ophthalmic solution) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | deacetylation? |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.011.431 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H15NO2 |
| Molar mass | 169.224 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Aceclidine (Glaucostat, Glaunorm, Glaudin) is a parasympathomimetic miotic agent used in the treatment of narrow angle glaucoma. It decreases intraocular pressure.
Adverse effects
Side effects of aceclidine include increased salivation and bradycardia (in excessive doses).
Mechanism of action
Aceclidine acts as a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist.[1]
See also
- Talsaclidine (drug with a similar structure)
- Muscarine
References
- ↑ Shannon HE, Hart JC, Bymaster FP, et al. (August 1999). "Muscarinic receptor agonists, like dopamine receptor antagonist antipsychotics, inhibit conditioned avoidance response in rats". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 290 (2): 901–7. PMID 10411607.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.