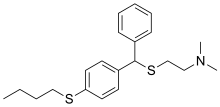
Captodiame
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.936 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H29NS2 |
| Molar mass | 359.59 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Captodiame (INN), also known as captodiamine, is an antihistamine sold under the trade names Covatine, Covatix, and Suvren which is used as a sedative and anxiolytic. The structure is related to diphenhydramine.[1]
A 2004 study suggested captodiame may be helpful in preventing benzodiazepine withdrawal syndrome in people discontinuing benzodiazepine treatment.[1]
In addition to its actions as an antihistamine, captodiamine has been found to act as a 5-HT2C receptor antagonist and σ1 receptor and D3 receptor agonist.[2] It produces antidepressant-like effects in rats.[2] However, captodiamine is unique among antidepressant-like drugs in that it increases brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in the hypothalamus but not in the frontal cortex or hippocampus.[2] This unique action may be related to its ability to attenuate stress-induced anhedonia and corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) signaling in the hypothalamus.[2]
Synthesis
The oxygen atom in these molecules can in many cases be dispensed with as well; substitution of sulfur for nitrogen affords a molecule whose salient biologic properties are those of a sedative and tranquilizer.
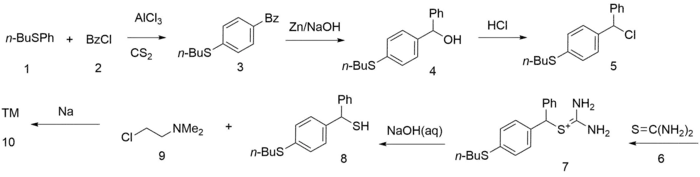
Friedel-Crafts acylation of the n-butyl ether of thiophenol with benzoyl chloride gives the corresponding benzophenone. Reduction of the ketone with zinc/NaOH followed by treatment with HCl in ether affords the benzhydryl chloride. Displacement of the halogen with thiourea gives, by reaction of the last at its most nucleophilic center, the isothiouronium salt. Hydrolysis of the salt leads to the sulfur analog of a benzhydrol. Alkylation of the sodium salt of this last with N-(2-chloroethyl)dimethylamine affords captodiame.
See also
References
- 1 2 Mercier-Guyon C, Chabannes JP, Saviuc P (2004). "The role of captodiamine in the withdrawal from long-term benzodiazepine treatment". Curr Med Res Opin. 20 (9): 1347–55. doi:10.1185/030079904125004457. PMID 15383182. Free full text with registration
- 1 2 3 4 Ring RM, Regan CM (October 2013). "Captodiamine, a putative antidepressant, enhances hypothalamic BDNF expression in vivo by synergistic 5-HT2c receptor antagonism and sigma-1 receptor agonism". J. Psychopharmacol. (Oxford). 27 (10): 930–9. doi:10.1177/0269881113497614. hdl:10197/4383. PMID 23863923.
| 5-HT1AR agonists | |
|---|---|
| GABAAR PAMs |
|
| Gabapentinoids (α2δ VDCC blockers) | |
| Antidepressants |
|
| Sympatholytics (Antiadrenergics) |
|
| Others | |
| |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||