Benperidol
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Anquil, Frenactil |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.521 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
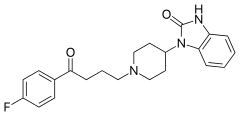
| Formula | C22H24FN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 381.451 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Benperidol, sold under the trade name Anquil[1] among others, is a drug which is a highly potent butyrophenone derivative. It is the most potent neuroleptic on the European market, with chlorpromazine equivalency as high as 75 to 100 (about 150 to 200% potency in terms of dose compared to haloperidol).[2] It is an antipsychotic, which can be used for the treatment of schizophrenia,[3] but it is primarily used to control hypersexuality syndromes[4] and is sometimes prescribed to sex offenders as a condition of their parole, as an alternative to anti-androgen drugs such as cyproterone acetate.[5]
Benperidol was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1961.
Synthesis
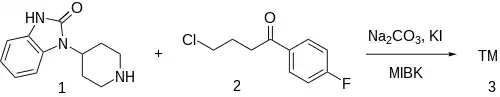
Benperidol synthesis:[6]
See also
- Timiperone has the same structure but thiourea instead of normal urea.
- Pimozide & Bezitramide (& Oxiperomide & Neflumozide) are also made from 4-(1-Benzimidazolinone)piperidine precursor
- Droperidol is self-same albeit with a tetrahydropyridine ring.
References
- ↑ Council A, Kuenssberg V (1974-02-01). "Benperidol - a drug for sexual offenders?". Drug and Therapeutics Bulletin. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd. 12 (3): 12. doi:10.1136/dtb.12.3.12. PMID 4457302. S2CID 44581451.
- ↑ Möller HJ, Müller WE, Bandelow (2001). Neuroleptika: pharmakologische Grundlagen, klinisches Wissen und therapeutisches Vorgehen; mit 136 Tabellen (in German). Wiss. Verlag-Ges. ISBN 3-8047-1773-X.
- ↑ Bobon J, Collard J, Lecoq R (October 1963). "[Benperidol and promazine: a "double blind" comparative study in mental geriatrics]". Acta Neurologica et Psychiatrica Belgica (in French). 63: 839–43. PMID 14092279.
- ↑ British National Formulary (49th), British Medical Association 2005 p 183
- ↑ Murray MA, Bancroft JH, Anderson DC, Tennent TG, Carr PJ (November 1975). "Endocrine changes in male sexual deviants after treatment with anti-androgens, oestrogens or tranquillizers". The Journal of Endocrinology. 67 (2): 179–88. doi:10.1677/joe.0.0670179. PMID 1107462.
- ↑ BE 626307 (1963 to Janssen), C.A. 60, 10690c (1964), corresp. to GB 989755.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.