Oxypertine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.291 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
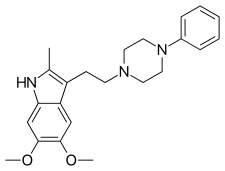
| Formula | C23H29N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 379.504 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Oxypertine (Equipertine, Forit, Integrin, Lanturil, Lotawin, Opertil) is an antipsychotic used in the treatment of schizophrenia.[1] It was also evaluated for the treatment of anxiety at a dosage of 20 mg per day.[2] Chemically, it is an indole and phenylpiperazine derivative.[3] Like reserpine and tetrabenazine, oxypertine depletes catecholamines, though not serotonin, possibly underlying its neuroleptic efficacy.[4] Its structure is similar to solypertine and milipertine.
See also
References
- ↑ Hall, Chapman and; Rhodes, P. H (1996). Dictionary of organic compounds. London: Chapman & Hall. ISBN 0-412-54090-8.
- ↑ Somohano MD, Broissin MC, Sobrino z A. [Clinical evaluation of oxypertine in anxiety conditions]. Neurol Neurocir Psiquiatr. 1976;17(3):171-80.
- ↑ Breulet M, Labar P, Delree C, Collard J, Bobon J (February 1968). "[Oxypertine, peperazine derivative of tryptophan with neuroleptic and dynamogenic properties]". Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg (in French). 68 (2): 116–27. PMID 4972600.
- ↑ Bak IJ, Hassler R, Kim JS (1969). "Differential monoamine depletion by oxypertine in nerve terminals. Granulated synaptic vesicles in relation to depletion of norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin". Zeitschrift für Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie. 101 (3): 448–62. doi:10.1007/BF00335580. PMID 5362847. S2CID 32583722.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.