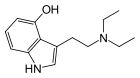
4-HO-DET
 | |
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H20N2O |
| Molar mass | 232.327 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 104 to 106 °C (219 to 223 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
4-HO-DET, also known as 4-hydroxy-diethyl-tryptamine, CZ-74, is a hallucinogenic drug and psychedelic compound of moderate duration. 4-HO-DET is a substituted tryptamine, structurally related to psilocin, ethocybin, and 4-HO-DIPT.
Analogs
The acetic acid ester of 4-HO-DET is known as 4-AcO-DET. The phosphoric acid ester of 4-HO-DET is known as 4-phosphoryloxy-DET, CEY-19, or ethocybin.
History
4-HO-DET received the lab code CZ-74 in the late 1950s by the inventors of the substance, Albert Hofmann and Franz Troxler. The substance was used together with its phosphoryloxy-analog ethocybin in human clinical trials in the 1960s by the German researchers Hanscarl Leuner and G. Baer.
Dosage
10–25 mg is the usual oral dosage for 4-HO-DET, while the acetate and phosphate esters are said to require a slightly higher dosage.
Effects
4-HO-DET produces entheogenic effects similar to LSD and psilocybin.
Drug prohibition laws
Sweden
Sveriges riksdags health ministry Statens folkhälsoinstitut classified 4-HO-DET as "health hazard" under the act Lagen om förbud mot vissa hälsofarliga varor (translated Act on the Prohibition of Certain Goods Dangerous to Health) as of Nov 1, 2005, in their regulation SFS 2005:733 listed as 4-hydroxi-N,N-diethyltryptamin (4-HO-DET), making it illegal to sell or possess.[1]
See also
- TiHKAL
- Indoles
References
External links
- TiHKAL 4-HO-DET information at Erowid
- 4-HO-DET entry in TiHKAL • info
- Ethacetin degradation