ECPLA
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ECYPLA |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H25N3O |
| Molar mass | 335.451 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
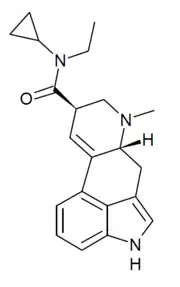
ECPLA (N-ethyl-N-cyclopropyllysergamide) is an analog of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) developed by Synex Synthetics. In studies in mice, it was found to have approximately 40% the potency of LSD.[2][3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Arrêté du 20 mai 2021 modifiant l'arrêté du 22 février 1990 fixant la liste des substances classées comme stupéfiants". www.legifrance.gouv.fr (in French). 20 May 2021.
- ↑ Halberstadt AL, Klein LM, Chatha M, Valenzuela LB, Stratford A, Wallach J, et al. (February 2019). "Pharmacological characterization of the LSD analog N-ethyl-N-cyclopropyl lysergamide (ECPLA)". Psychopharmacology. 236 (2): 799–808. doi:10.1007/s00213-018-5055-9. PMC 6848745. PMID 30298278.
- ↑ Wagmann L, Richter LH, Kehl T, Wack F, Bergstrand MP, Brandt SD, et al. (July 2019). "In vitro metabolic fate of nine LSD-based new psychoactive substances and their analytical detectability in different urinary screening procedures" (PDF). Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 411 (19): 4751–4763. doi:10.1007/s00216-018-1558-9. PMID 30617391. S2CID 58615418.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.