Veralipride
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Agreal, Agradil |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.060.376 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
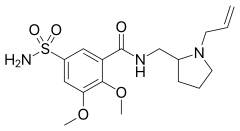
| Formula | C17H25N3O5S |
| Molar mass | 383.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Veralipride (Agreal, Agradil) is a benzamide neuroleptic medicine indicated in the treatment of vasomotor symptoms associated with the menopause.[1] It was first authorised for use in 1979. Veralipride has never gained approval in the United States.
In September 2006, it was withdrawn from the Spanish market. As a result, the European Commission referred the matter to the European Medicines Agency (EMA). On July 2007, the EMA recommended the withdrawal of marketing authorisations for veralipride.[2]
See also
- Typical antipsychotic
- Benzamide
References
- ↑ Carranza-Lira S (September 2010). "Actual status of veralipride use". Clinical Interventions in Aging. 5: 271–6. doi:10.2147/cia.s12640. PMC 2938034. PMID 20852674.
- ↑ "Overall Summary of the Scientific Evaluation of Medicinal Products Containing Veralipride" (PDF). EMEA.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.