Phenprobamate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 5 - 8 hours |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.552 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
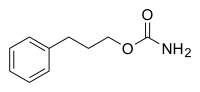
| Formula | C10H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 179.22 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Phenprobamate (Gamaquil, Isotonil) is a centrally acting skeletal muscle relaxant, with additional sedative and anticonvulsant effects.[1] Overdose is similar to barbiturates. Its mechanism of action is probably similar to meprobamate. Phenprobamate has been used in humans as an anxiolytic, and is still sometimes used in general anesthesia and for treating muscle cramps and spasticity. Phenprobamate is still used in some European countries, but it has generally been replaced by newer drugs. Phenprobamate is metabolized by oxidative degradation of the carbamate group and ortho-hydroxylation of the benzene ring, and is eliminated in urine by the kidneys.
Doses range from 400 to 800 mg, up to 3 times a day.
References
- ↑ Demir B, Demir Y, Aksoy I, Kilic OH, Gucyetmez V, Savas HA (June 2015). "Phenprobamate dependence: a case report". Addictive Behaviors. 45: 232–3. doi:10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.01.037. PMID 25727392.
Further reading
- Tasdemir HA, Yildiran A, Islek I, Sancak R, Dilber C (May 2002). "Haemoperfusion may be useful in phenprobamate and polypharmacy intoxication of paediatric patients". Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation. 17 (5): 941. doi:10.1093/ndt/17.5.941. PMID 11981094.
External links
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.