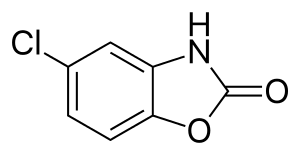
Chlorzoxazone
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | klor zox' a zone[1] |
| Trade names | Lorzone, Paraflex, Muscol, others |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Muscle relaxant[1] |
| Main uses | Low back pain, muscle spasms[1] |
| Side effects | Dizziness, sleepiness, headache, tremor[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Onset of action | With 1 hr[2] |
| Duration of action | Up to 4 hr[2] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a682577 |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | Well absorbed |
| Protein binding | 13–18% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1.1 hr |
| Excretion | Urine (<1%) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H4ClNO2 |
| Molar mass | 169.56 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Chlorzoxazone, sold under the brand names Lorzone among others, is a muscle relaxant used to treat low back pain and muscle spasms.[1] Benefits are moderate.[1] It is not useful for neurological problems such as cerebral palsy.[2] It is taken by mouth.[1] Effects begin within an hour and last for up to 4 hours.[2]
Common side effects include dizziness, sleepiness, headache, and tremor.[1] Other side effects may include liver problems and angioedema.[1][2] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[2] It works at the level of the spinal cord and brain.[2]
Chlorzoxazone was approved for medical use in the United States in 1958.[1] It is available as a generic medication.[1] In the United States 60 pills of 500 mg costs about 18 USD as of 2022.[5] As of 2017 it remains widely used.[1]
Medical uses
Dosage
The usual recommended dose in adults is 250 to 750 mg by mouth three to four times daily, reducing the dose to lowest effective level once a response occurs.[1] It is typically given for 1 to 4 weeks only.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 "Chlorzoxazone". Archived from the original on 8 May 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Chlorzoxazone Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 28 November 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ↑ "Parafon DSC- chlorzoxazone tablet". DailyMed. 9 February 2010. Archived from the original on 16 March 2021. Retrieved 5 November 2020.
- ↑ "Lorzone- chlorzoxazone tablet". DailyMed. 21 June 2019. Archived from the original on 12 November 2020. Retrieved 5 November 2020.
- ↑ "Chlorzoxazone Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 5 November 2016. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
Further reading
- Dong DL, Luan Y, Feng TM, Fan CL, Yue P, Sun ZJ, Gu RM, Yang BF (2006). "Chlorzoxazone inhibit contraction of rat thoracic aorta". Eur J Pharmacol. 545 (2–3): 161–6. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.063. PMID 16859676.
- Park J, Kim K, Park P, Ha J (2006). "Effect of high-dose aspirin on CYP2E1 activity in healthy subjects measured using chlorzoxazone as a probe". J Clin Pharmacol. 46 (1): 109–14. doi:10.1177/0091270005282635. PMID 16397290. S2CID 20092326.
- Wan J, Ernstgård L, Song B, Shoaf S (2006). "Chlorzoxazone metabolism is increased in fasted Sprague-Dawley rats". J Pharm Pharmacol. 58 (1): 51–61. doi:10.1211/jpp.58.1.0007. PMC 1388188. PMID 16393464.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- Chloroxazone Safety Data Sheet Archived 2019-07-12 at the Wayback Machine
- D.F. Marsh, U.S. Patent 2,895,877 (1959)