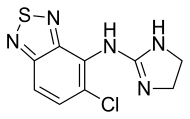
Tizanidine
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /taɪˈzænɪdiːn/ tye-ZAN-i-deen |
| Trade names | Zanaflex, Sirdalud, and others |
| Other names | 4-Chloro-N-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazol-2-yl)-8-thia-7,9-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]nona-2,4,6,9-tetraen-5-amine |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth (tablets, capsules) |
| Defined daily dose | 12 mg[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a601121 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | ~40%[2] |
| Protein binding | ~30% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP1A2, 95%) |
| Elimination half-life | 2.54 hours (tizanidine), 20–40 hours (inactive metabolites)[2] |
| Excretion | Urine (60%), feces (20%) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H8ClN5S |
| Molar mass | 253.71 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Tizanidine, sold under the brand name Zanaflex among others, is a medication used to treat muscle spasticity due to spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis.[3] Effectiveness appears similar to baclofen or diazepam.[4] It is taken by mouth.[5]
Common side effects include dry mouth, sleepiness, weakness, and dizziness.[5] Serious side effects may include low blood pressure, liver problems, psychosis, and QT prolongation.[5] It is unclear if use in pregnancy and breastfeeding is safe.[6] It is an α2-adrenergic agonist and how it works is not entirely clear.[5]
Tizanidine was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996.[5] It is available as a generic medication.[3] A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 3.45 £ as of 2019.[3] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$4.20.[7] In 2017, it was the 89th most prescribed medication in the United States, with more than nine million prescriptions.[8][9]
Medical uses
Tizanidine has been found to be as effective as other antispasmodic drugs and is more tolerable than baclofen and diazepam.[4]
Dosage
The defined daily dose is 12 mg by mouth.[1]
Side effects
Side effects include dizziness, drowsiness, weakness, nervousness, hallucinations, depression, vomiting, dry mouth, constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, heartburn, increased muscle spasms, back pain, rash, sweating, and a tingling sensation in the arms, legs, hands, and feet.[10]
Interactions
Concomitant use of tizanidine and moderate or potent CYP1A2 inhibitors (such as zileuton, certain antiarrhythmics (amiodarone, mexiletine, propafenone, verapamil), cimetidine, famotidine, aciclovir, ticlopidine and oral contraceptives) is contraindicated. Concomitant use of tizanidine with fluvoxamine, a potent CYP1A2 inhibitor in humans, resulted in a 33-fold increase in the tizanidine AUC (plasma drug concentration-time curve).[2] For this reason both fluvoxamine and tizanidine should not be taken at the same time. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics such as moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, and ciprofloxacin should also be avoided due to an increased serum concentration of tizanidine when administered concomitantly.[11] Tizanidine has the potential to interact with other central nervous system depressants. Alcohol should be avoided, particularly as it can upset the stomach. The CNS-depressant effects of tizanidine and alcohol are additive.[2] Caution with the following interactions:[12][13][14]
- antibiotics such as enoxacin, gatifloxacin, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin, moxifloxacin, ofloxacin, sparfloxacin, trovafloxacin , or norfloxacin;
- blood pressure medications such as clonidine, guanabenz, guanfacine (Tenex), or methyldopa;
- heart rhythm medications such as amiodarone (Cordarone, Pacerone), mexiletine (Mexitil), propafenone (Rhythmol), and verapamil (Calan, Covera, Isoptin).
Pharmacology
Tizanidine is an α2 agonist closely related to clonidine. It has approximately one tenth to one fifteenth of the pressure lowering effect of clonidine. The relation between the α2 receptor agonism and the spasmolytic action is still not fully understood.[15]
Route of administration
Tizanidine is available as a tablet or capsule. Capsules may be opened and sprinkled on food. However, this may change the absorption of the medication compared to taking the capsule whole.[16]
Chemistry
It has a volume of distribution of 2.4 L/kg following intravenous administration.[2]
Society and culture
Cost
A month supply in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about 3.45 £ as of 2019.[3] In the United States the wholesale cost of this amount is about US$4.20.[7] In 2017, it was the 89th most prescribed medication in the United States, with more than nine million prescriptions.[8][9]
.svg.png.webp) Tizanidine costs (US)
Tizanidine costs (US).svg.png.webp) Tizanidine prescriptions (US)
Tizanidine prescriptions (US)
References
- 1 2 "WHOCC - ATC/DDD Index". www.whocc.no. Archived from the original on 2 March 2019. Retrieved 6 September 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Zanaflex (tizanidine hydrochloride) Capsules and Tablets for Oral Use. Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Acorda Therapeutics Inc. Ardsley, NY 10502. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 March 2015. Retrieved 1 September 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 British national formulary : BNF 76 (76 ed.). Pharmaceutical Press. 2018. p. 1094. ISBN 9780857113382.
- 1 2 Kamen L, Henney HR, Runyan JD (February 2008). "A practical overview of tizanidine use for spasticity secondary to multiple sclerosis, stroke, and spinal cord injury". Current Medical Research and Opinion. 24 (2): 425–39. doi:10.1185/030079908X261113. PMID 18167175.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Tizanidine Hydrochloride Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 16 June 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ↑ "Tizanidine Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Warnings". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 3 December 2018. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- 1 2 "NADAC as of 2019-02-27". Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Archived from the original on 6 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- 1 2 "The Top 300 of 2020". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 18 March 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- 1 2 "Tizanidine - Drug Usage Statistics". ClinCalc. Archived from the original on 8 July 2020. Retrieved 11 April 2020.
- ↑ pmhdev. "Page not available". PubMed Health. Archived from the original on 11 November 2012. Retrieved 4 September 2017.
- ↑ "Tizanidine Uses, Dosage, Side Effects – Drugs.com". drugs.com. Archived from the original on 14 July 2017. Retrieved 4 September 2017.
- ↑ NHS Wales (2011). "Tizanidine (Zanaflex) Gwent Primary Care Prescribing Guidance" (PDF). Aneurin Bevan University Health Board. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 October 2012. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ↑ "Tizanidine package leaflet: Information for the user" (PDF). Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (UK). 2016. Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 September 2018. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ↑ "Zanaflex (tizanidine hydrochloride) dose, indications, adverse effects, interactions... from PDR.net". www.pdr.net. Archived from the original on 16 September 2018. Retrieved 16 September 2018.
- ↑ Katzung, Bertram G. (30 November 2017). Basic & clinical pharmacology. Katzung, Bertram G. (Fourteenth ed.). New York. p. 487. ISBN 9781259641152. OCLC 1015240036.
- ↑ "Tizanidine: MedlinePlus Drug Information". medlineplus.gov. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 4 October 2019. Retrieved 29 October 2019.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |