EVT-201
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
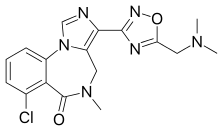
| Formula | C17H17ClN6O2 |
| Molar mass | 372.81 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
EVT-201 is a benzodiazepine derivative drug and partial positive allosteric modulator of the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor.[1] It has 2–4-fold higher functional affinity for the α1 subunit relative to the α2, α3, and α5 subunits and significantly less intrinsic activity in comparison to currently-marketed benzodiazepines and the Z-drugs.[2] Despite the lower efficacy, EVT-201 still shows effectiveness in the treatment of insomnia, and it is thought that the lower efficacy may result in fewer side effects, such as motor incoordination.[2] The drug was originally developed by Roche, based on preclinical data, as a non-sedating anxiolytic, but was found to produce sedation in humans in phase I clinical trials. For this reason, it was subsequently licensed to Evotec, which is now developing it for the treatment of insomnia.[2] As of 2007, EVT-201 has completed phase II clinical trials for this indication, with positive findings reported.[3] As of August 2015, Phase II development is ongoing in China.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Guilleminault C (2010). Sleep Medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 574–. ISBN 978-1-4377-1836-2.
- 1 2 3 Monti JM, Pandi-Perumal SR, Möhler H (28 September 2010). GABA and Sleep: Molecular, Functional and Clinical Aspects. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 50–51. ISBN 978-3-0346-0226-6.
- ↑ Plunkett JW (September 2007). Plunkett's Biotech & Genetics Industry Almanac 2008: Biotech & Genetics Industry Market Research, Statistics, Trends & Leading Companies. Plunkett Research, Ltd. pp. 311–. ISBN 978-1-59392-087-6.
- ↑ "Drug Profile: EVT 201". AdisInsight. Adis International Ltd, part of Springer Science+Business Media. Retrieved 30 November 2015.
External links