Lemborexant
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Dayvigo |
| Other names | E-2006 |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Orexin antagonist |
| Main uses | Trouble sleeping[1] |
| Side effects | Poor coordination, sleep paralysis, sleep walking, misuse, suicide[1][2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Typical dose | 5 mg OD[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | 94%[1] |
| Metabolism | Liver (major: CYP3A4, minor: CYP3A5)[1] |
| Metabolites | M10[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 17–19 hours[1] |
| Excretion | Feces: 57.4%[1] Urine: 29.1%[1] |
| Chemical and physical data | |
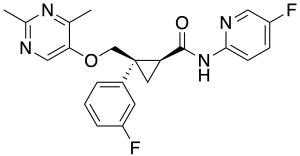
| Formula | C22H20F2N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 410.425 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Lemborexant, sold under the brand name Dayvigo, is a medication used to treat trouble sleeping.[1] It may be used for trouble falling asleep or staying asleep.[1] It is taken by mouth.
Common side effects include sleepiness.[1] Other side effect may include poor coordination, sleep paralysis, sleep walking, misuse, and suicide.[1][2] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[4] It is an orexin receptor blocker.[1]
Lemborexant was approved for medical use in the United States in 2019.[1] In the United States it costs about 320 USD per month as of 2021.[5] In the United States it is a Schedule IV controlled substance.[2]
Medical uses
Lemborexant is used in the treatment of insomnia.[1]
Dosage
The typical dose is 5 mg before going to bed.[1]
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Lemborexant is a dual antagonist of the orexin OX1 and OX2 receptors.[6][7][8]
Pharmacokinetics
The time to peak levels of lemborexant is 1 to 3 hours.[1] A high-fat and high-calorie meal has been found to delay the time to peak levels by 2 hours.[1] Its plasma protein binding in vitro is 94%.[1] Lemborexant is metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP3A5.[1] The elimination half-life of lemborexant is 17 to 19 hours.[1] The medication is excreted in feces (57%) and to a lesser extent urine (29%).[1]
History
In June 2016, Eisai initiated Phase III clinical trials in the United States, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Poland, Spain and the UK.[9]
In December 2019, lemborexant was approved for use in the United States based on results from the SUNRISE 1 and SUNRISE 2 Phase III clinical trials.[10][11]
Society and culture
Generic names
Lemborexant is the generic name of the drug and its INN.
Brand names
Lemborexant is sold under the brand name Dayvigo.[1]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 "Dayvigo- lemborexant tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 24 June 2021. Retrieved 17 June 2021.
- 1 2 3 "Lemborexant Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 24 September 2020. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- 1 2 "Dayvigo". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 23 July 2021. Archived from the original on 5 September 2021. Retrieved 5 September 2021.
- ↑ "Lemborexant (Dayvigo) Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 27 August 2021. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ↑ "Dayvigo Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Retrieved 21 November 2021.
- ↑ Christopher, John A (2014). "Small-molecule antagonists of the orexin receptors". Pharmaceutical Patent Analyst. 3 (6): 625–638. doi:10.4155/ppa.14.46. ISSN 2046-8954. PMID 25489915.
- ↑ Cristoph Boss, Catherine Ross (2015). "Recent Trends in Orexin Research – 2010 to 2015". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 25 (15): 2875–2887. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.05.012. PMID 26045032.
- ↑ Boss, Christoph (2014). "Orexin receptor antagonists – a patent review (2010 to August 2014)". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 24 (12): 1367–1381. doi:10.1517/13543776.2014.978859. ISSN 1354-3776. PMID 25407283. S2CID 21106711.
- ↑ "Lemborexant". Specialist Pharmacy Service. Archived from the original on 7 November 2017. Retrieved 5 November 2017.
- ↑ "FDA Approves Dayvigo (lemborexant) for the Treatment of Insomnia in Adult Patients". Drugs.com. 23 December 2019. Archived from the original on 11 January 2020. Retrieved 10 January 2020.
- ↑ "Drug Trials Snapshot: Dayvigo". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 December 2019. Archived from the original on 11 August 2020. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
External links
- Abad VC, Guilleminault C (September 2018). "Insomnia in Elderly Patients: Recommendations for Pharmacological Management". Drugs Aging. 35 (9): 791–817. doi:10.1007/s40266-018-0569-8. PMID 30058034. S2CID 51866276.
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |