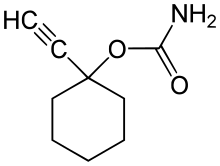
Ethinamate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.355 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 167.208 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Ethinamate (Valamin, Valmid) is a short-acting carbamate-derivative sedative-hypnotic medication used to treat insomnia. Regular use leads to drug tolerance, and it is usually not effective for more than 7 days. Prolonged use can lead to dependency.
Ethinamate has been replaced by other medicines (particularly benzodiazepines), and it is not available in the Netherlands, the United States or Canada.
It is a schedule IV substance.[1]
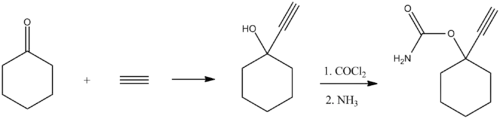
Synthesis
Ethinamate (1-ethynylcyclohexanone carbamate) is synthesized by combining acetylene with cyclohexanone to make 1-ethynylcyclohexanol, and then transforming this into a carbamate by the subsequent reaction with phosgene, and later with ammonia. Some lithium metal or similar is used to make the acetylene react with the cyclohexanone in the first step.[2][3]
References
- ↑ Lowry WT, Garriot JC (1979). "Ethinamate". Forensic Toxicology: Controlled Substances and Dangerous Drugs. Boston, MA: Springer US. p. 215. ISBN 978-1-4684-3444-6.
- ↑ US 2816910, Pfeiffer H, Junkman K, "Esters of carbamic acid and a method of making same", issued 17 December 1957, assigned to Schering AG
- ↑ DE 1021843, Emde H, Grimme W, "Verfahren zur Herstellung des Allophanats des 1-AEthinylcyclohexanols-(1)", issued 2 January 1958, assigned to Rheinpreussen AG