Radiation proctitis
| Radiation proctitis | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Radiation proctopathy, Radiation associated vascular ectasias (RAVE) | |
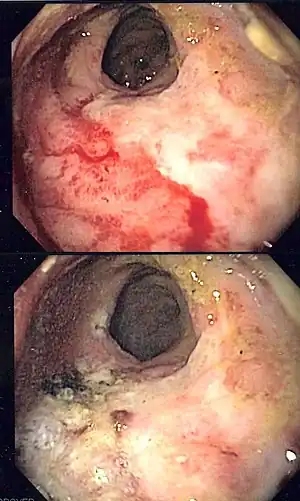 | |
| Endoscopic image of radiation associated vascular ectasias (RAVE) before and after therapy with argon plasma coagulation. | |
| Symptoms | Pelvic pain, tenesmus, diarrhea, urgency, hematochezia |
| Complications | Anemia, perforation, fistulae |
| Types | Acute (<3 months after radiation) and Chronic (>3 months after radiation) |
| Causes | Pelvic radiation for cancer |
| Diagnostic method | Colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Infectious proctitis, inflammatory bowel disease |
| Treatment | Endoscopy with argon plasma coagulation, bipolar electrocautery, radiofrequency ablation |
Radiation proctitis or radiation proctopathy is condition characterized by damage to the rectum after exposure to x-rays or other ionizing radiation as a part of radiation therapy.[1] Radiation proctopathy may occur as acute inflammation called "acute radiation proctitis" (and the related radiation colitis) or with chronic changes characterized by radiation associated vascular ectasiae (RAVE) and chronic radiation proctopathy.[2][1] Radiation proctitis most commonly occurs after pelvic radiation treatment for cancers such as cervical cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, and rectal cancer. RAVE and chronic radiation proctopathy involves the lower intestine, primarily the sigmoid colon and the rectum, and was previously called chronic radiation proctitis, pelvic radiation disease and radiation enteropathy.[3]
Signs and symptoms
Acute radiation proctopathy often causes pelvic pain, diarrhea, urgency, and the urge to defecate despite having an empty colon (tenesmus).[4] Hematochezia and fecal incontinence may occur, but are less common.[4] Chronic radiation damage to the rectum (>3 months) may cause rectal bleeding, incontinence, or a change in bowel habits secondary. Severe cases may lead to with strictures or fistulae formation.[5][4] Chronic radiation proctopathy can present at a median time of 8-12 months following radiation therapy.[4]
Histopathology
Acute radiation proctopathy occurs due to direct damage of the lining (epithelium) of the colon.[1] Rectal biopsies of acute radiation proctopathy show superficial depletion of epithelial cells and acute inflammatory cells located in the lamina propria.[4] By contrast, rectal biopsies of RAVE and chronic radiation proctopathy demonstrates ischemic endarteritis of the submucosal arterioles, submucosal fibrosis, and neovascularization.[4]
Diagnosis
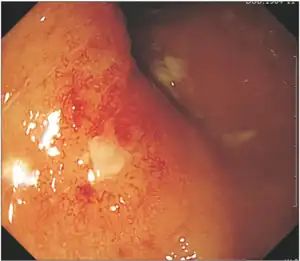
Where chronic radiation proctopathy or RAVE is suspected, a thorough evaluation of symptoms is essential. Evaluation should include an assessment of risk factors for alternate causes of proctitis, such as C. difficile colitis, NSAID use, and travel history.[6] Symptoms such as diarrhea and painful defecation need to be systematically investigated and the underlying causes each carefully treated.[7] Testing for parasitic infections (amebiasis, giardiasis) and sexually transmitted infections (Neisseria gonorrhoeae and herpes simplex virus) should be considered.[6] The location of radiation treatment is important, as radiation directed at regions of the body other than the pelvis (eg brain, chest, etc) should not prompt consideration of radiation proctopathy.[6]
Endoscopy is the mainstay of diagnosis for radiation damage to the rectum, with either colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy. RAVE is usually recognized by the macroscopic appearances on endoscopy characterized by vascular ectasias.[8] Mucosal biopsy may aid in ruling out alternate causes of proctitis, but is not routinely necessary and may increase the risk of fistulae development.[6] Telangiectasias are characteristic and prone to bleeding.[3] Additional endoscopic findings may include pallor (pale appearance), edema, and friability of the mucosa.
Classification
Radiation proctitis can occur a few weeks after treatment, or after several months or years:
- Acute radiation proctitis — symptoms occur in the first 3 months after therapy.[4] These symptoms include diarrhea and the urgent need to defecate.
- Radiation associated vascular ectasias (RAVE) and Chronic radiation proctopathy — previously known as "chronic radiation proctitis" occur 3-6 months after the initial exposure. RAVE is characterized by rectal bleeding, chronic blood loss and anemia. Chronic radiation proctopathy is characterized by urgency, change in stool caliber and consistency and increased mucus. Severe cases may present with fistulas and strictures which are rare.[2]
Treatment
Several methods have been studied in attempts to lessen the effects of radiation proctitis. Acute radiation proctitis usually resolves without treatment after several months. When treatment is necessary, symptoms often improve with hydration, anti-diarrheal agents, and discontinuation of radiation.[4] Butyrate enemas may also be effective.[9][10]
In contrast, RAVE and chronic radiation proctopathy usually is not self-limited and often requires additional therapies.[4] These include sucralfate, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, corticosteroids, metronidazole, argon plasma coagulation, radiofrequency ablation and formalin irrigation.[1][3][11] The average number of treatment sessions with argon plasma coagulation to achieve control of bleeding ranges from 1 to 2.7 sessions.[4]
In rare cases that do not respond to medical therapy and endoscopic treatment, surgery may be required. Overall, less than 10 percent of individuals with radiation proctopathy require surgery.[4] In addition, complications such as obstruction and fistulae may require surgery.
Epidemiology
Up to 30 percent of individuals who receive pelvic radiation therapy for cancer may develop radiation proctopathy.[4]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Babb RR (1996). "Radiation proctitis: a review". Am. J. Gastroenterol. 91 (7): 1309–11. PMID 8677984.
- 1 2 Mahmood, Sultan; Bollipo, Steven; Steele, Scott; Bristow, Robert G.; Choudhury, Ananya; Oakland, Kathryn; Martin, Jarad (2020-10-20). "It's All the RAVE: Time to Give up on the "Chronic Radiation Proctitis" Misnomer". Gastroenterology. 160 (3): 635–638. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.054. ISSN 0016-5085. PMID 33096102. Archived from the original on 2021-08-10. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- 1 2 3 Fuccio L, Guido A, Andreyev HJ (2012). "Management of intestinal complications in patients with pelvic radiation disease". Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 10 (12): 1326–1334.e4. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2012.07.017. PMID 22858731.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Lee, JK; Agrawal, D; Thosani, N; Al-Haddad, M; Buxbaum, JL; Calderwood, AH; Fishman, DS; Fujii-Lau, LL; Jamil, LH; Jue, TL; Khashab, MA; Law, JK; Naveed, M; Qumseya, BJ; Sawhney, MS; Storm, AC; Yang, J; Wani, SB (August 2019). "ASGE guideline on the role of endoscopy for bleeding from chronic radiation proctopathy". Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 90 (2): 171–182.e1. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2019.04.234. PMID 31235260.
- ↑ Mahmood, Sultan; Bollipo, Steven; Steele, Scott; Bristow, Robert G.; Choudhury, Ananya; Oakland, Kathryn; Martin, Jarad (2020-10-20). "It's All the RAVE: Time to Give up on the "Chronic Radiation Proctitis" Misnomer". Gastroenterology. 160 (3): 635–638. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.054. ISSN 0016-5085. PMID 33096102. Archived from the original on 2021-08-10. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- 1 2 3 4 Weiner, JP; Wong, AT; Schwartz, D; Martinez, M; Aytaman, A; Schreiber, D (21 August 2016). "Endoscopic and non-endoscopic approaches for the management of radiation-induced rectal bleeding". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 22 (31): 6972–86. doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i31.6972. PMC 4988305. PMID 27610010.
- ↑ Andreyev, HJ; Muls, AC; Norton, C; Ralph, C; Watson, L; Shaw, C; Lindsay, JO (January 2015). "Guidance: The practical management of the gastrointestinal symptoms of pelvic radiation disease". Frontline Gastroenterology. 6 (1): 53–72. doi:10.1136/flgastro-2014-100468. PMC 4283714. PMID 25580207.
- ↑ Mahmood, Sultan; Bollipo, Steven; Steele, Scott; Bristow, Robert G.; Choudhury, Ananya; Oakland, Kathryn; Martin, Jarad (2020-10-20). "It's All the RAVE: Time to Give up on the "Chronic Radiation Proctitis" Misnomer". Gastroenterology. 160 (3): 635–638. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.054. ISSN 0016-5085. PMID 33096102. Archived from the original on 2021-08-10. Retrieved 2022-07-16.
- ↑ Vernia P, Fracasso PL, Casale V, et al. (October 2000). "Topical butyrate for acute radiation proctitis: randomised, crossover trial". Lancet. 356 (9237): 1232–1235. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02787-2. PMID 11072942. S2CID 42326854.
- ↑ Hille A, Herrmann MK, Kertesz T, et al. (December 2008). "Sodium butyrate enemas in the treatment of acute radiation-induced proctitis in patients with prostate cancer and the impact on late proctitis. A prospective evaluation". Strahlenther Onkol. 184 (12): 686–692. doi:10.1007/s00066-008-1896-1. PMID 19107351. S2CID 24755382.
- ↑ Ma TH, Yuan ZX, Zhong QH, Wang HM, Qin QY, Chen XX, Wang JP, Wang L (2015). "Formalin irrigation for hemorrhagic chronic radiation proctitis". World J. Gastroenterol. 21 (12): 3593–8. doi:10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3593. PMC 4375582. PMID 25834325.
External links
| Classification |
|---|