Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome
| Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Ectodermal dysplasia, anhidrotic, with cleft lip/palate[1] | |
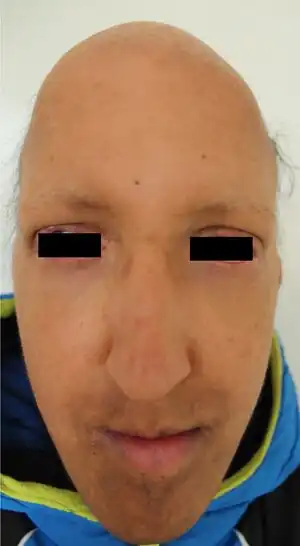 | |
| Rapp–Hodgkin Syndrome: frontal bossing, short philtrum, thin upper lip, mildly dysmorphic auricles and prognathism | |
Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome was formerly thought to be a unique autosomal dominant disorder due to a P63 gene mutation. However, it was recently shown to the same disease as Hay–Wells syndrome.[2]
It was first characterized in 1968.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Rapp–Hodgkin syndrome". The Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center. NIH. Archived from the original on 24 January 2017. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ↑ Clements SE, Techanukul T, Holden ST, et al. (September 2010). "Rapp–Hodgkin and Hay–Wells ectodermal dysplasia syndromes represent a variable spectrum of the same genetic disorder". Br. J. Dermatol. 163 (3): 624–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09859.x. PMID 20491771. S2CID 44866051.
- ↑ Rapp RS, Hodgkin WE (December 1968). "Anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia: autosomal dominant inheritance with palate and lip anomalies". J. Med. Genet. 5 (4): 269–72. doi:10.1136/jmg.5.4.269. PMC 1468665. PMID 5713637.
Further reading
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.