This article was co-authored by wikiHow Staff. Our trained team of editors and researchers validate articles for accuracy and comprehensiveness. wikiHow's Content Management Team carefully monitors the work from our editorial staff to ensure that each article is backed by trusted research and meets our high quality standards.
This article has been viewed 354,550 times.
Learn more...
When working in Oracle, you may find that some of your records have duplicates. You can delete these duplicate rows by identifying them and using its RowID, or row address. Before you begin, you should create a backup table in case you need to reference them after you have deleted records.
Steps
Identifying your Duplicate
-
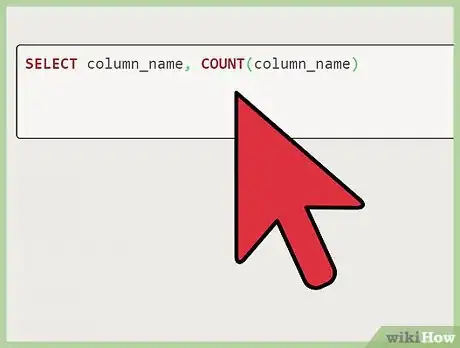
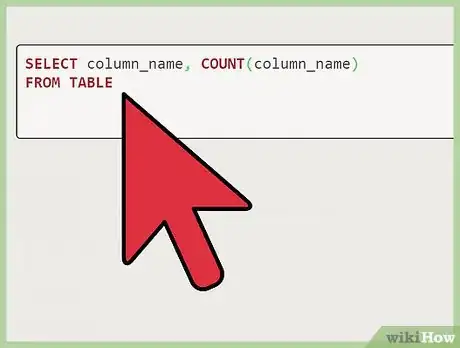
1Identify the duplicate. In this case, identify the example duplicate, "Alan." Make sure that the records you are trying to delete are actually duplicates by entering the SQL below.
-
2Identifying from a column named "Names." In the instance of a column named "Names," you would replace "column_name" with Names.Advertisement
-
3Identifying from other columns. If you were trying to identify the duplicate by a different column, for example the age of Alan rather than his name, you would enter "Ages" in the place of "column_name" and so on.
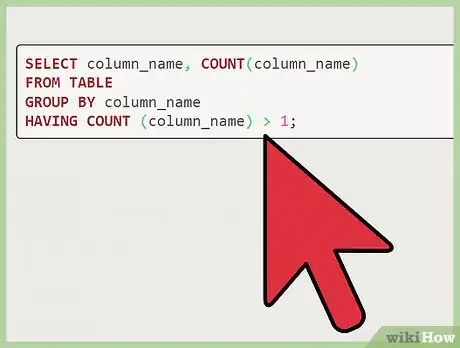
select column_name, count(column_name) from table group by column_name having count (column_name) > 1;
Deleting a Single Duplicate
-
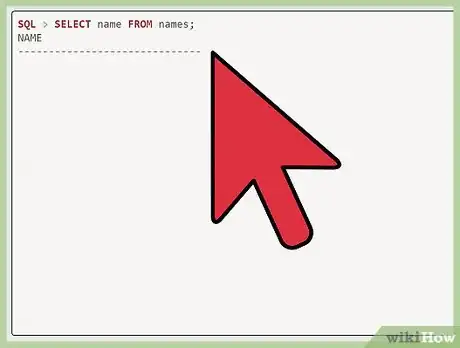
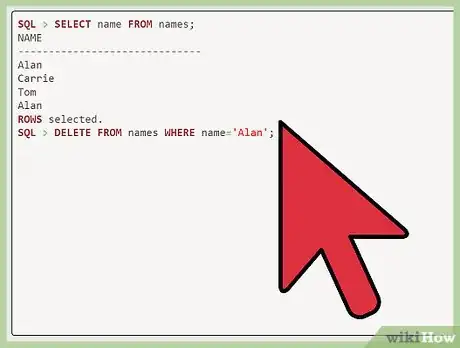
1Select "name from names." After "SQL," which stands for Standard Query Language, enter "select name from names."
-
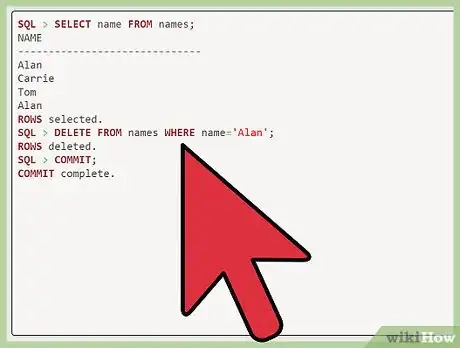
2Delete all of the rows with the duplicate name. After "SQL," enter "delete from names where name='Alan';." Note that capitalization is important here, so this will delete all of the rows named "Alan." After "SQL," enter "commit."[1]
-
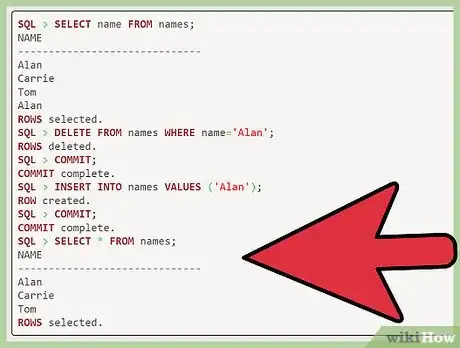
3Renter the row without a duplicate. Now that you have deleted all rows with the example name "Alan," you can insert one back by entering "insert into name values ('Alan');." After "SQL," enter "commit" to create your new row.
-
4See your new list. Once you have completed the above steps, you can check to make sure you no longer have duplicate records by entering "select * from names."
SQL > select name from names; NAME ------------------------------ Alan Carrie Tom Alan rows selected. SQL > delete from names where name='Alan'; rows deleted. SQL > commit; Commit complete. SQL > insert into names values ('Alan'); row created. SQL > commit; Commit complete. SQL > select * from names; NAME ------------------------------ Alan Carrie Tom rows selected.
Deleting Multiple Duplicates
-
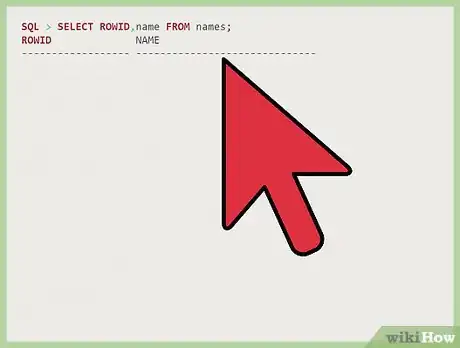
1Select the RowID you want to delete. After "SQL," enter "select rowid, name from names;."
-
2Delete the duplicate. After "SQL," enter "delete from names a where rowid > (select min(rowid) from names b where b.name=a.name);" to delete duplicate records.[2]
-
3Check for duplicates. After you have completed the above, commands check to see if you still have duplicate records by entering "select rowid,name from names;" and then "commit."
SQL > select rowid,name from names; ROWID NAME ------------------ ------------------------------ AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAA Alan AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAB Alan AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAC Carrie AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAD Tom AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAF Alan rows selected. SQL > delete from names a where rowid > (select min(rowid) from names b where b.name=a.name ); rows deleted. SQL > select rowid,name from names; ROWID NAME ------------------ ------------------------------ AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAA Alan AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAC Carrie AABJnsAAGAAAdfOAAD Tom rows selected. SQL > commit; Commit complete.
Deleting Rows with Columns
-
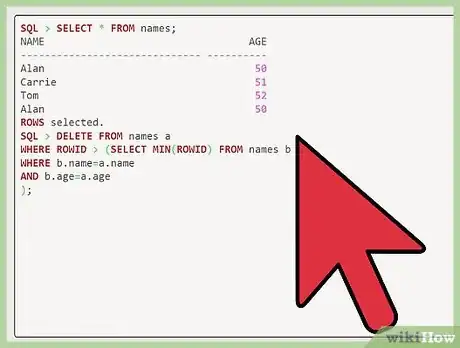
1Select your rows. After "SQL," enter "select * from names;" to see your rows.
-
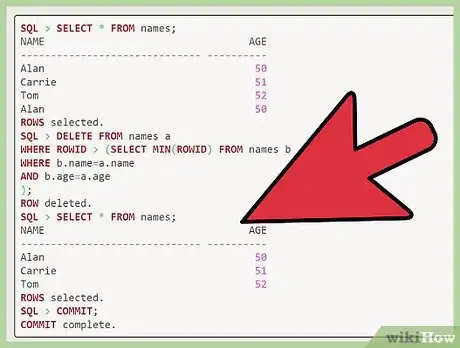
2Delete duplicate rows by identifying their column. After "SQL'" enter "delete from names a where rowid > (select min(rowid) from names b where b.name=a.name and b.age=a.age);" to delete the duplicate records.[3]
-
3Check for duplicates. Once you have completed the above steps, enter "select * from names;" and then "commit" in order to check that you have deleted the duplicate records successfully.
SQL > select * from names; NAME AGE ------------------------------ ---------- Alan 50 Carrie 51 Tom 52 Alan 50 rows selected. SQL > delete from names a where rowid > (select min(rowid) from names b where b.name=a.name and b.age=a.age ); row deleted. SQL > select * from names; NAME AGE ------------------------------ ---------- Alan 50 Carrie 51 Tom 52 rows selected. SQL > commit; Commit complete.
Our Most Loved Articles & Quizzes
Warnings
- Create a backup table in your own sign-in that you can use to show what was there before any delete occurred (in case there are any questions).
SQL > create table alan.names_backup as select * from names; Table created.
⧼thumbs_response⧽
References
About This Article
To delete duplicate records in Oracle, start by making sure the records are actually duplicates by entering the Standard Query Language, or SQL. After entering “SQL,” search for what you want to delete, like “delete from names where name = ‘Alan.’” Then, enter “commit” for this command to take effect. Once you’ve deleted all the rows with the example name “Alan,” create your new row by entering “insert into name values (‘Alan’)” followed by "commit." When you've completed these steps, check to make sure you no longer have duplicates by entering “select * from names.” To learn how to delete multiple duplicates, keep reading!