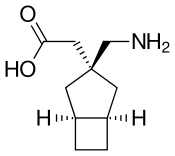
PD-217,014
PD-217,014 is a drug developed by Pfizer and related to gabapentin, which similarly binds to the α2δ calcium channels (1 and 2). It was developed as a potentially more potent successor to gabapentin and pregabalin, along with several other analogues such as atagabalin and 4-methylpregabalin, but while PD-217,014 produces visceral analgesic effects in animal studies with higher potency and efficacy than gabapentin, it was not developed further for clinical use because of its comparatively more complex synthesis, compared to other related analogues.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H17NO2 |
| Molar mass | 183.251 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
| Calcium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Potassium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sodium |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chloride |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Transient receptor potential channel modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.