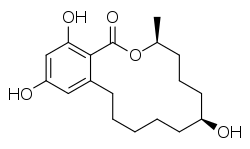
Taleranol
Taleranol (INN, USAN) (developmental code name P-1560), or teranol, also known as β-zearalanol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the resorcylic acid lactone group related to mycoestrogens found in Fusarium spp which was never marketed.[1][2] It is the β epimer of zeranol (α-zearalanol) and is a major metabolite of zeranol but with less biological activity.[1][3][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | P-1560; Teranol; β-Zearalanol |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.729 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H26O5 |
| Molar mass | 322.401 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
- α-Zearalenol
- β-Zearalenol
- Zearalanone
- Zearalenone
References
- J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 350–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- Yildiz F (16 December 2009). Advances in Food Biochemistry. CRC Press. pp. 233–. ISBN 978-1-4200-0769-5.
- Yu L, Wang S, Sun BG (28 October 2014). Food Safety Chemistry: Toxicant Occurrence, Analysis and Mitigation. CRC Press. pp. 240–. ISBN 978-1-4665-9795-2.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.