COVID-19 pandemic in Zamboanga Peninsula
The COVID-19 pandemic in Zamboanga Peninsula is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The virus reached Zamboanga Peninsula, Philippines on March 24, 2020, when the first case of the disease was confirmed in Zamboanga City. All provinces including the cities of Zamboanga and Isabela have recorded at least a single case.
| COVID-19 pandemic in Zamboanga Peninsula | |
|---|---|
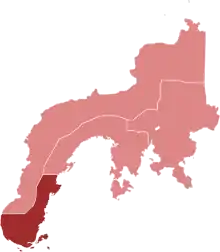 1000–4999 confirmed
500–999 confirmed
100–499 confirmed
50–99 confirmed
10–49 confirmed
1–9 confirmed | |
| Disease | COVID-19 |
| Virus strain | SARS-CoV-2 |
| Location | Zamboanga Peninsula |
| First outbreak | Wuhan, Hubei, China |
| Index case | Zamboanga City |
| Arrival date | March 24, 2020 (2 years, 7 months, 1 week and 1 day) |
| Confirmed cases | 18,753 |
| Recovered | 16,416 |
Deaths | 367 |
| Government website | |
| ro9 | |
Timeline
The first case in the Zamboanga Peninsula was confirmed in Zamboanga City on March 24, 2020. The case was that of 29-year-old male resident who arrived in the city on March 13 after visiting Metro Manila.[1] The province of Zamboanga del Sur announced its first two cases on March 30. The day prior, the provincial government appealed passengers of Philippine Airlines flight PR2889 from Manila-Ozamis on March 14 to go to the nearest health facility if they develop COVID-19 symptoms.[2]
No new province reported COVID-19 cases until May 2020. On May 4, the first COVID-19 case was confirmed in Zamboanga del Norte, that of a case of a 63-year-old Norwegian who arrived in Dipolog on March 2. The patient was admitted to a private hospital in the city on April 26 after complaining of chest pain and was airlifted to Metro Manila on May 2.[3][4]
In late April 2020, Zamboanga City began to experience a rapid rise in the number of cases in its prisons.[5][6] By May 4, most of Zamboanga City's cases are from inmates and personnel of the Zamboanga City Reformatory Center. Three of the confirmed cases are Bureau of Jail Management and Penology personnel while two inmates has died from COVID-19.[7] An outbreak at the prison has already been declared by the city government.[8]
Zamboanga Sibugay reported its first case on June 24, that of a student in Imelda who arrived in the town from Cebu City on June 24.[9] The city of Isabela in Basilan, which is also part of the Zamboanga Peninsula region despite the rest of the province under the Bangsamoro region, confirmed its first case on June 29, that of a 25-year-old female who arrived in the city from Manila on June 18.[10]
Impact
The launch of a new flight route serving Zamboanga City and Kota Kinabalu of the Philippine Airlines set on March 31 was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Business plans and partnership between Zamboanga City-based businessmen and their counterparts in Sabah has been put on hold over the drastic rise of cases in the Zamboanga City in early May 2020.[11]
The COVID-19 outbreak has affected the Zamboanga City Reformatory Center which houses about 3.3 thousand inmates and about a hundred personnel despite only being designed to accommodate 400 detainees.[8]
Fish canneries in Zamboanga City announced that it would reduce the production of canned fish in the Philippines by 50–60% due to difficulties encountered following the implementation of a city-wide lockdown. The Industrial Group of Zamboanga reported that most of its workers experienced difficulties in reporting to work, despite the company offering free shuttle services, due to the wide presence of checkpoints across barangays. Fish canneries in the city also had to reduce outputs due to the deliverers of fish from Zamboanga Sibugay and Zamboanga del Norte experiencing difficulties in entering the city, as visitors are required to undergo a 14-day quarantine. This prompted most canneries to discourage deliveries.[12]
Response
The whole of Zamboanga Peninsula has been placed under enhanced community quarantine (ECQ) by April 2020.[13] When the ECQ was lifted on May 1, Zamboanga City was allowed by the Inter-Agency Task Force for the Management of Emerging Infectious Diseases to remain under ECQ until May 15.[14]
In May 2020, the Zamboanga City Medical Center COVID-19 testing laboratory started operating.[15]
Notes
- Breakdown of confirmed cases is according to the COVID-19 Case Tracker of the Department of Health.
References
- "Zamboanga City records first COVID-19 case". ABS-CBN News. March 25, 2020. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- "Zamboanga del Sur records first 2 coronavirus cases". Rappler. March 30, 2020. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- Laput, Gualberto (May 5, 2020). "Zamboanga del Norte records 1st coronavirus case". Rappler. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- Diestro, Dynah (May 6, 2020). "Bisitang Norwegian, naitalang unang kaso ng COVID-19 sa Dipolog City". ABS-CBN News (in Tagalog). Retrieved December 18, 2020.
- Pareño, Roel (May 2, 2020). "18 inmates, 1 jail employee test positive for COVID-19 in Zambo". The Philippine Star. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- Cepeda, Mara (May 3, 2020). "Zamboanga City's coronavirus cases spike as more inmates get infected". Rappler. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- "Mindanao's COVID-19 positives surge to 249 as Zamboanga jail cases rise to 50". The Mindanao Daily Mirror. May 4, 2020. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- Pareño, Roel (May 3, 2020). "COVID-19 outbreak declared in Zamboanga City jail". The Philippine Star. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- "Zamboanga Sibugay records first COVID-19 case". CNN Philippines. June 24, 2020. Retrieved June 24, 2020.
- Lacastesantos, Leizel (June 29, 2020). "Isabela City, Basilan records first coronavirus case". ABS-CBN News. Retrieved July 6, 2020.
- Fabian, Nikko (May 6, 2020). "Worry over spike in Zamboanga Covid-19 cases". Daily Express. Retrieved May 7, 2020.
- Alipala, Julie (March 30, 2020). "Fish canneries cut output by 50–60%". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Retrieved April 4, 2020.
- "Situational Report No.8 of the National Task Force (NTF) for COVID-19" (PDF). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. April 8, 2020. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 26, 2020. Retrieved April 8, 2020.
- Pareño, Roel; Mendez, Christina (May 3, 2020). "IATF OKs Albay, Zamboanga ECQ extension". The Philippine Star. Retrieved May 3, 2020.
- "First COVID-19 testing facility in Zamboanga now operational". ABS-CBN News. May 8, 2020. Retrieved May 8, 2020.
.jpg.webp)
